How to use the Get API in Elasticsearch
Introduction
The Elastic’s Get API library has the power to return an index’s data after you make a GET request to a cluster in Elasticsearch. There are two ways to accomplish this. Either use the Kibana Console User Interface (UI) or the cURL library to do it.
GET requests enable you to return document data in an Elasticsearch cluster fast. This step-by-step tutorial on how to use Elastic’s Get API by making cURL requests to return JSON data about an Elasticsearch index and its documents will show you exactly how to do it.
Prerequisites
Elasticsearch – Install the latest compatible version for your operating system, then run the application.
Kibana – If you’re using Kibana to make
GETrequests, install the application. The latest one for your operating system is recommended. Next, run the service.Check that the service is running by navigating to the domain on your server or to the
localhost:9200. When the page loads up, you should see the Elasticsearch cluster’s JSON (Javascript Object Notation) response.
Here’s an example of using the browser tab to get a webpage JSON response from Elasticsearch on port 9200
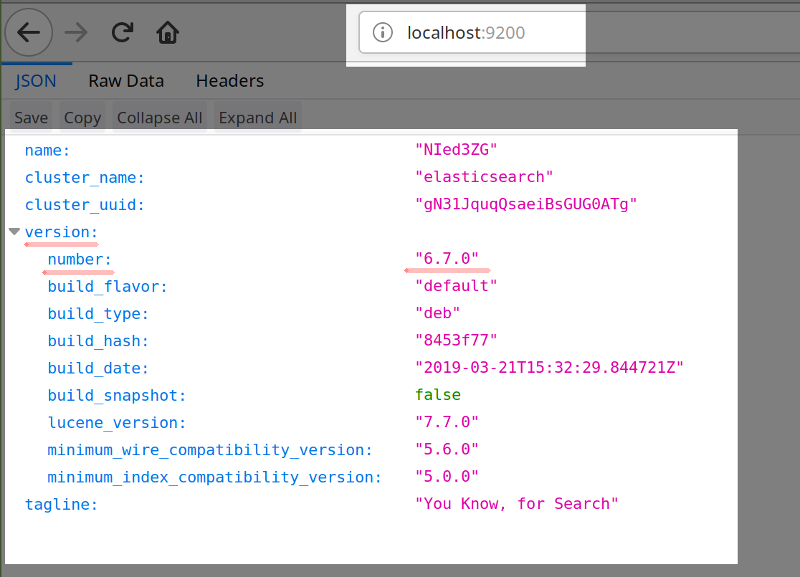
You can do the same for Kibana to verify if the service is running. Navigate to port
5601and the Kibana UI will load.Either one of these two replies below means the server is not running.
No response
“404 Not Found”
To run Elastic Stack in Linux type this:
sudo service {SERVICE_NAME} start.A great way to see every service that is currently running on all ports is to go to a UNIX terminal and run the command: netstat.
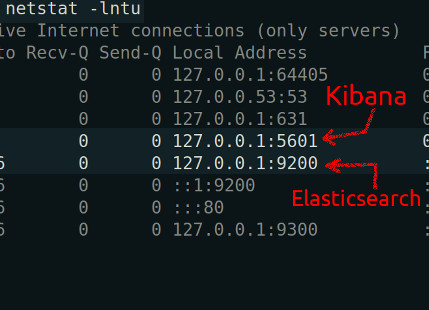
You can use the ‘netstat’ command in a UNIX terminal to print out a list of all the services running on different ports:
1 | netstat -lntu |
Network Statistics netstat verifies active services. Use it to check the ports to determine if Kibana and Elasticsearch are running.
Here’s an example showing both Kibana and Elasticsearch are running on the servers.
It’s easy to create an Index in Elasticsearch
- Through the HTTP method,
GET, is how the Get API sends requests to return data from the Elasticsearch cluster. So, first, you’ll need an index with some documents so that it can do that.
Use the Kibana Console UI to create an Elasticsearch Index
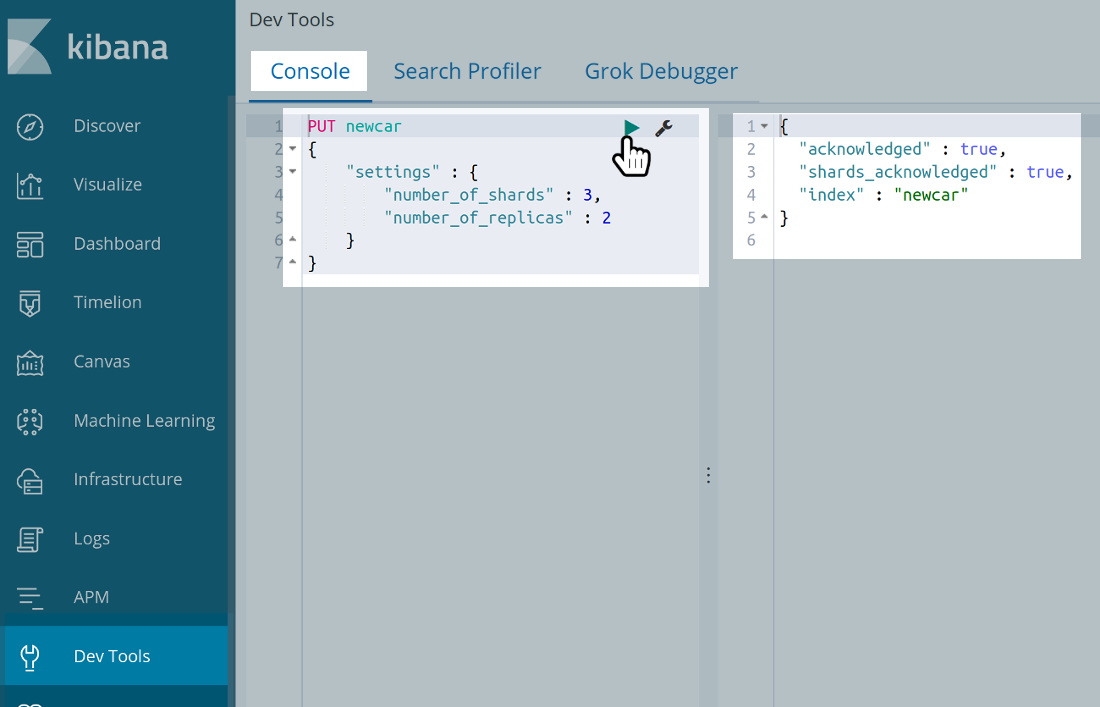
- To make a new index in Elasticsearch in Kibana, use the
PUTrequest.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | PUT newcar { "settings" : { "number_of_shards" : 3, "number_of_replicas" : 2 } } |
Next, look at the right panel of the Kibana UI. It worked if the JSON response returns "acknowledged".
- While making the request, in the body of the JSON, it’s a good idea to indicate the number of shards, including the replicas per shard. If you wait until after you make the request, it can be challenging and takes time to change the settings in the index.
Use cURL to Create an Index in Elasticsearch
To start making cURL requests in elasticsearch and create an index in Elasticsearch, you’ll need to do these three things.
- Identify the domain on the server
- Elasticsearch port
- Header information for JSON objects passed in the body of the requests. One example is
"Content-Type".
This is what the cURL version request in Kibana looks like:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/newcar?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' { "settings" : { "number_of_shards" : 3, "number_of_replicas" : 2 } } ' |
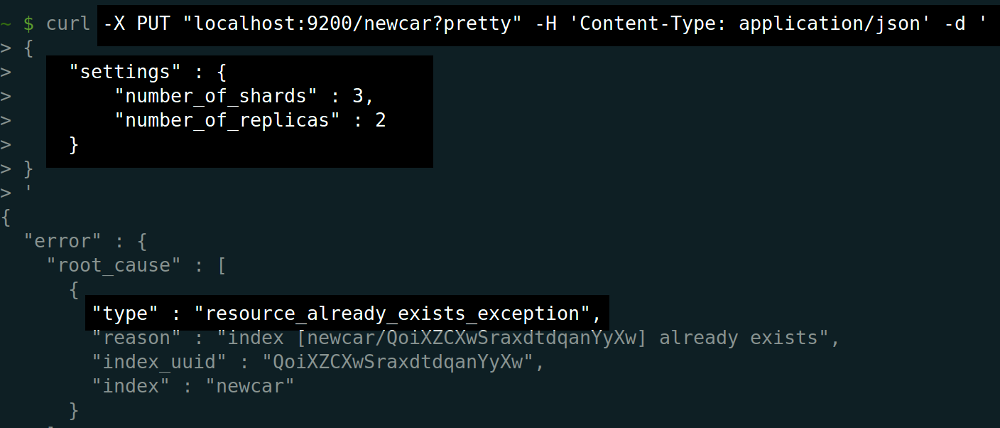
If you try to create an index on the same Elasticsearch cluster, an error will be raised. To avoid raising errors like that, do the following:
Use your IP address or server’s domain name instead of
localhostif you’re not using a localhost server to run an Elasticsearch cluster.Check the default setting in the file
elasticsearch.yml. Use port9200for the Elasticsearch port.
Trying to create an Elasticsearch Index and receiving a resource_already_exists_exception
Put documents in an Index in Elasticsearch using cURL
Use the PUT request for putting documents into an Elasticsearch index. You’re using a cURL request to get an Elasticsearch index.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | curl -X PUT "localhost:9200/newcar/two_door/2?pretty" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' { "make" : "Toyota", "model" : "Corolla", "color" : "white", "year" : 1984 } ' |
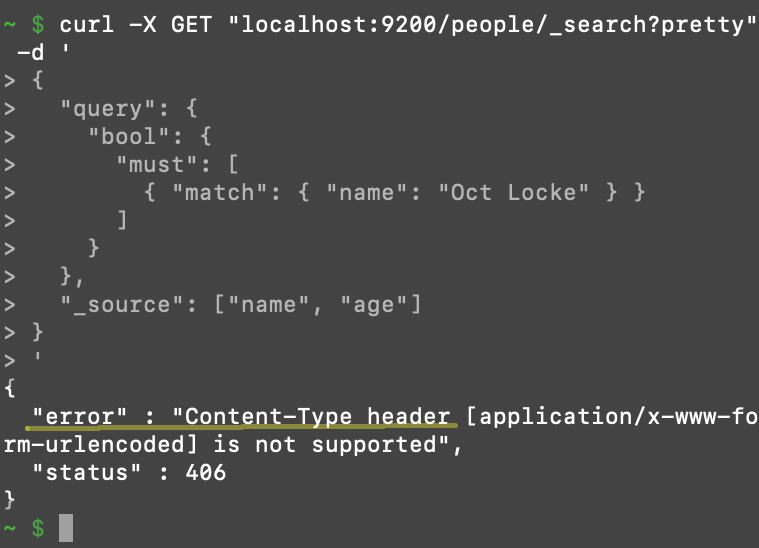
NOTE: Starting with Elastic Stack version 6.0, all cURL requests with JSON content body objects must be specified explicitly. They must have an option -H 'Content-Type: application/json in the header. Otherwise, it will return with a 406 Content-Type header error response.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | # IN ES v6.0 or > THIS cURL REQUEST WILL RETURN A 406 ERROR: # It's missing: -H 'Content-Type: application/json' curl -X GET "localhost:9200/people/_search?pretty" -d ' { "query": { "bool" : { "must" : { "match" : { "name" : "Joe Schmöe" } } } } } ' |
An example of the 406 Content Type header error is below. Type the command curl --help for assistance with header errors.
Learn more about how the Get API works
Unless you change the state of the document or index in an Elasticsearch cluster with a POST or PUT request, the HTTP GET method results should be the same every time.
RESTful APIs like
GET,POST, andPUTare among those operations commonly used for making web applications. They can do one of the following: create, retrieve, update, or delete (CRUD).You’re ready to make
GETrequests using Elasticsearch GET API to return JSON documents that are in the index. The requests are made to the Elastiscsearch cluster.An easy way to accomplish this is to use the parameter
"id"of the document you want to pass and pass it in the header to make a request.You won’t have to wait for the update because as soon as the data is viewable, the API automatically refreshes the data.
An Example of Using a GET Request in Elasticsearch
- Here’s an example of using the
GETAPI. We have an index callednewcar. We want to get a JSON document from that index. Other particulars are: - Document type =
two_door - Reference Arguments to pass =
"_id"of2
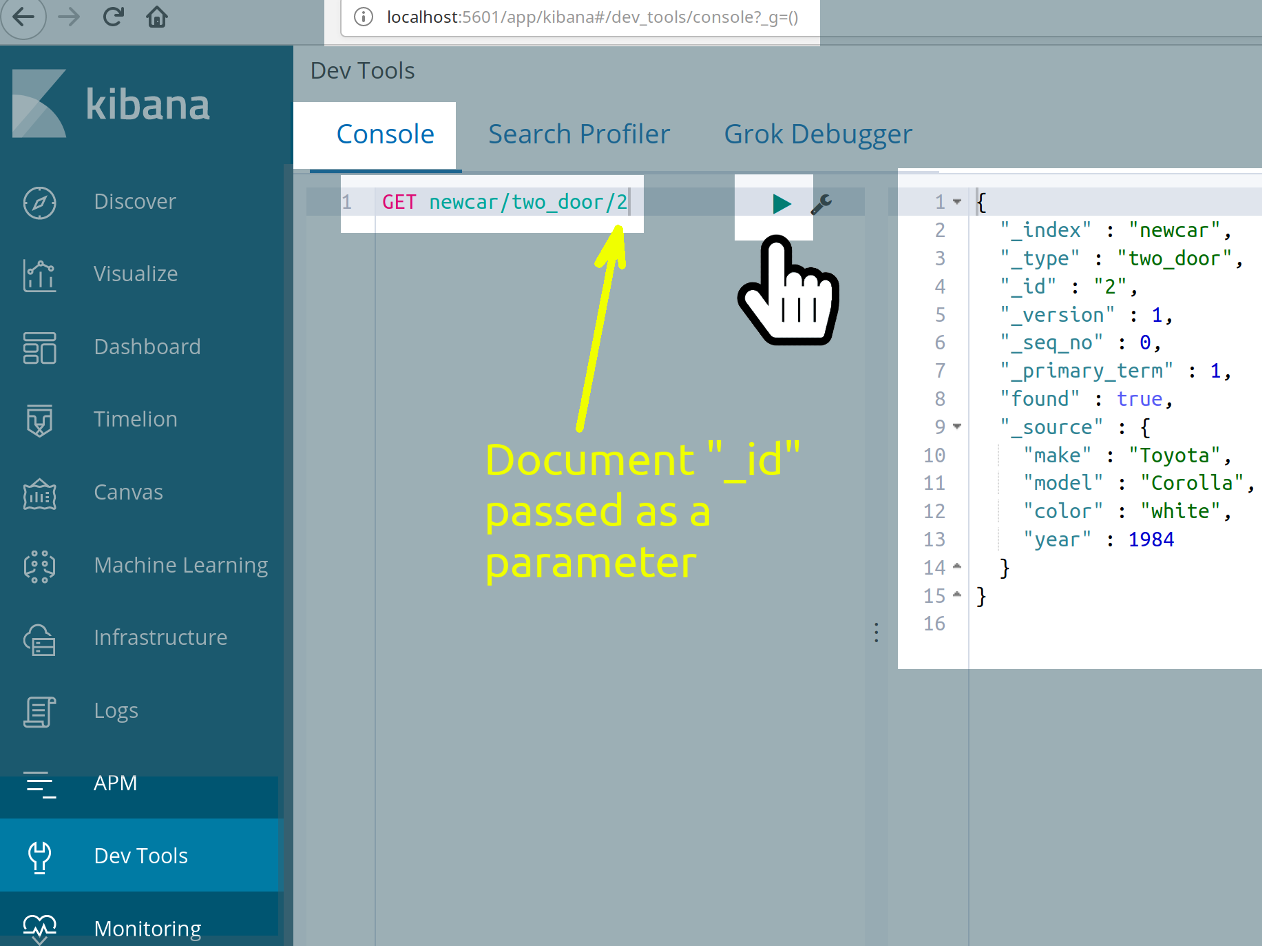
Use the Kibana Console UI and pass GET to get a JSON document from the index. Reference Arguments "_id" of 2
1 | GET newcar/two_door/2 |
- This is what you should see when the JSON object is returned.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | { "_index" : "newcar", "_type" : "two_door", "_id" : "2", "_version" : 1, "_seq_no" : 0, "_primary_term" : 1, "found" : true, "_source" : { "make" : "Toyota", "model" : "Corolla", "color" : "white", "year" : 1984 } } |
Look for the "found" field. The JSON object body shows true next to the"found" field as the booleen value in this example. That’s a good sign that you made the request correctly.
Making a cURL curl request to get an Elasticsearch document. Here’s how to GET a document with an "_id" of 2 in Elasticsearch:
 * Since there is a header but there isn’t a JSON object “body” in the example, you won’t need to pass the
* Since there is a header but there isn’t a JSON object “body” in the example, you won’t need to pass the Content-Type header.
1 2 3 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/newcar/two_door/2" # ...or # curl -XGET "http://{DOMAIN_NAME}:{DIFFERENT_PORT}/newcar/toyota/2/_source" |
No need for quotation marks either.
1 | curl -X GET localhost:9200/newcar/two_door/2 |
..however, if you include quotation marks, it will make it easier for people to read.
1 | curl -X GET "localhost:9200/newcar/two_door/2" |
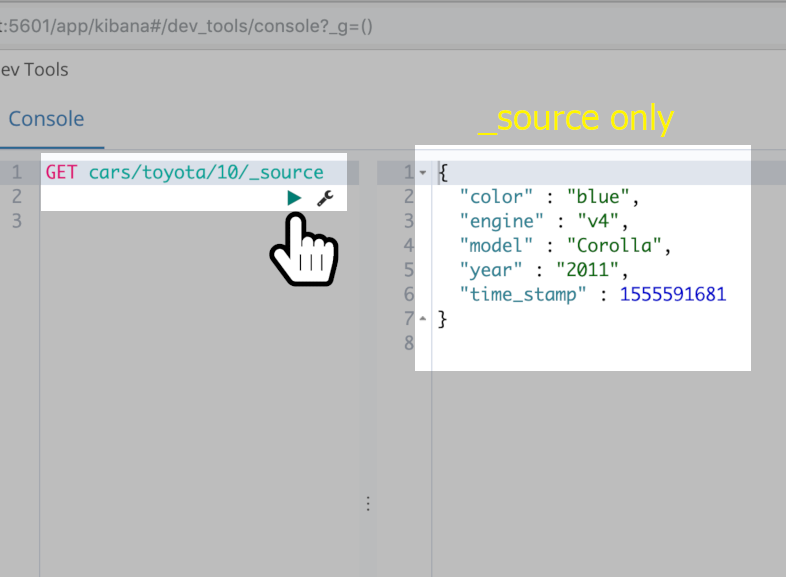
Here’s how to just get a document’s _source data
- To get the data without the metadata (such as
_version,_type,_id, and the like), you can get the document’s_sourcefield data. To do this use endpoint/{index}/{type}/{id}/_source.
1 | GET cars/toyota/10/_source |
Get just the _source fields and values that go with them for an Elasticsearch document
This example shows an explicit option to get certain fields only.
The
_sourcein the JSON object body is returned.This is what it looks like in cURL:
1 2 3 | curl -X GET "http://localhost:9200/newcar/toyota/2/_source" # ...or # curl -XGET "http://{DOMAIN_NAME}:{ALTERNATE_PORT}/newcar/toyota/2/_source" |
Conclusion
Making Get requests is the heart of data retrieval. You’ve learned in this tutorial the steps on how to create an index in Kibana Console UI and cURL. Next, you discovered covered how to use the ‘GET’ RESTful API to retrieve data from a JSON document in an Elastisearch index. You also found out how to address errors should they occur. This tutorial also showed you how to get only a document’s source data and how the Get API works in general. You can now use the Elasticsearch Get API library often, confidently, and effectively. For more information about the Get API, review Elastic’s official documentation.
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started



