How To Make The Kibana Service Start Automatically
Introduction
Kibana is a data analytics and data visualization product that’s part of the Elastic Stack. Although it’s designed to work with Elasticsearch, it’s a separate product that needs to be installed separately. While the product is sometimes run as a background daemon service, Kibana can also be run in a terminal in the foreground.
Kibana can be installed and run in several different ways, depending on the operating system being used:
All Linux Distributions: Archive Packages — .tar, .gz
Windows: MSI Installer, or ZIP Archive Packages — .zip
Ubuntu and Debian: Debian Packages —.deb
Red Hat, CentOS, and Fedora: RPM Packages — .rpm
In many cases, you may want Kibana to start up automatically when your system boots up. This tutorial will show how to set up an automatic start for Kibana when your system or server restarts.
Prerequisites:
Before we talk about how to make the Kibana service start automatically, it’s important to make sure certain prerequisites are in place. For this task, there a few key system requirements:
- Oracle’s JDK 8, Elasticsearch, and Kibana must be installed (or running as a service from a folder) on your machine or server. You can run the following commands in a terminal window to make sure the services are installed and running:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | # to get the Java version running on the machine: java -version # make a cURL request to the Elasticsearch cluster curl -X GET 'localhost:9200' # or domain name instead of 'localhost' # make a cURL request to the Kibana server curl -X GET 'localhost:5601' # should return nothing if port is occupied |
- If Elasticsearch and Kibana are configured to run on custom ports, other than their respective
9200and5601default ports, then you’ll need to specify them in the cURL requests. To find out what ports these services run on, check the respective YAML configuration files for Elasticsearch and Kibana.
Terminal commands to make sure than Java 8, Elasticsearch, and Kibana are installed and working:
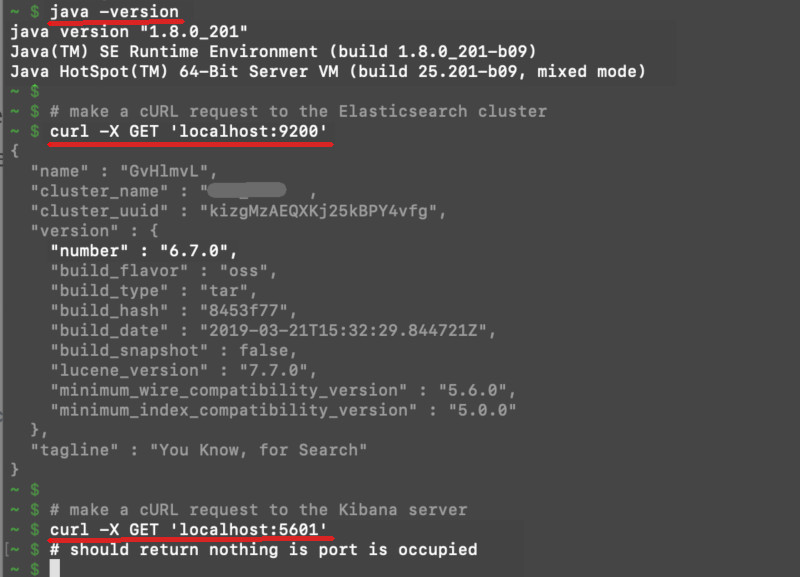
NOTE: The major versions of Elasticsearch and Kibana need to match to ensure compatibility (e.g. You’ll need to use version 6.x of Kibana if you’re running Elasticsearch version 6.x).
- Keep in mind that Kibana requires that you have Elasticsearch version 1.4.4 or newer installed.
Determine the service management framework for the OS running Kibana
The first step in making Kibana start automatically is to determine the service management framework for the OS that’s running Kibana. Linux, Windows, and macOS all use different service management frameworks to start, stop, and restart the various Elastic products.
- If Kibana and Elasticsearch are installed on macOS, then you’ll use the
launchdservice (through Homebrew) to start the services automatically. - Most Linux distributions (including some Red Hat distributions like RHEL7 and CentOS7) use the
systemdservices framework to run background daemons. - Other Linux distributions also use
SysV; RPM-based systems in particular tend to use theupstartservice framework. - In any UNIX-based (macOS or Linux) terminal you can also use the
pscommand to see which service framework is running:
1 | ps -p 1 |
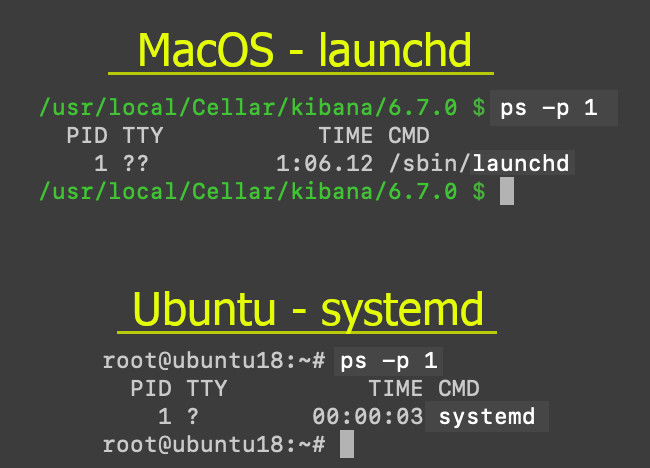
Check the service management for Debian Linux:
If you’re running the Elastic Stack on a Debian-based server (such as Ubuntu or Debian), you can use one of these commands to make sure that it uses systemd:
1 2 3 | dpkg -S /sbin/init # ..or: dpkg -l | grep systemd |
These commands should return a response that contains either systemd or sysv in it.
Service Management Frameworks on Red Hat Linux:
If you’re working with a Red Hat version of Linux that uses the rpm command to install packages, you can use the following command to determine if the service management is systemd or upstart:
1 | rpm -qf /sbin/init |
The output should contain the name of one of the two service management frameworks.
NOTE: Some older versions of Linux and UNIX-based operating systems may be using sysvinit.
Start Kibana automatically in Linux
Once you’ve determined which service management framework is being used, you can perform the next steps to make Kibana start automatically when your system reboots.
Check the service logs at var/log/kibana to monitor when the service starts and stops.
Start Kibana automatically using thesystemd service:
Most Debian-based distributions of Linux use systemd to start daemon services. Use the following commands to load the Kibana daemon and have the service start up at boot time:
1 2 | sudo /bin/systemctl daemon-reload sudo /bin/systemctl enable kibana.service |
Start Kibana automatically using the SysV service:
If the Linux OS uses the SysV framework, use the following command to have it start the service at boot-up time:
1 | sudo update-rc.d kibana defaults 95 10 |
Start the Kibana service automatically in macOS with Homebrew
The brew installation of Kibana should start the service automatically when the system reboots. If it doesn’t happen, you use Brew’s tap command instead:
1 2 3 | brew tap homebrew/services brew services start kibana # or brew services restart kibana |
Using the brew command to start Kibana automatically on macOS
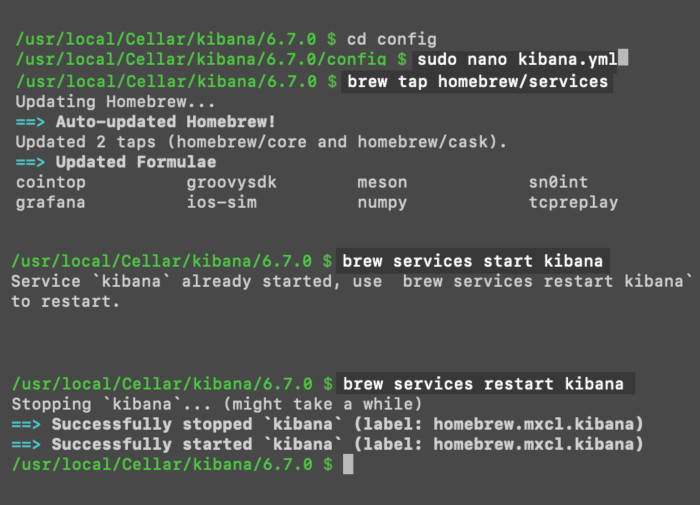
If you’re still having issues getting this working, check the YAML files in the Cellar directory to confirm that Kibana is configured properly:
1 | /usr/local/Cellar/kibana/ |
Run Kibana as a background daemon in Windows
If Kibana is running on Windows, you can just type run in the search bar, then type services or manage and open up the “Manage Services” window. Look for “Kibana” listed on the right-hand side of that window, and double-click it to edit it (you can also right-click the service and click “Properties”). Click on the Startup Type dropdown menu for Kibana, and select Automatic. Finally, click OK or Apply at the bottom right-hand corner of the window.
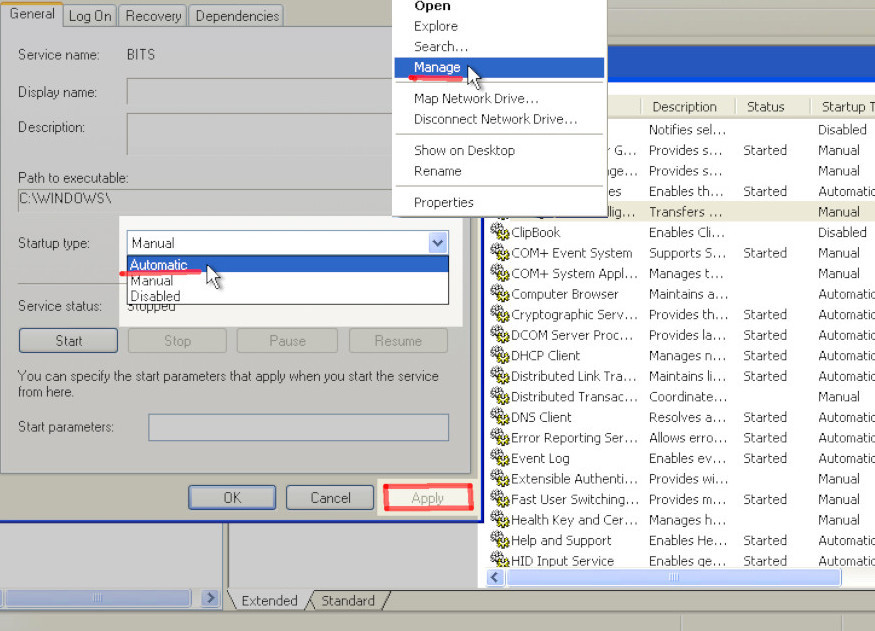
When you’re done, close the Services window. The next time Windows restarts, the Kibana service should start up automatically.
Conclusion:
Kibana is a powerful tool that allows you to analyze and visualize your Elasticsearch data in new ways. It can be helpful to have Kibana start up automatically when your server or system boots up. In this article, we explained how to set up an automatic start for Kibana in several different operating systems. With these step-by-step instructios, you should have no trouble making the Kibana service start automatically no matter what OS you’re using.
automatic start kibana daemon service kibana
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started



