How to Fix the RequestsDependencyWarning Elasticsearch with Python Import Error
Introduction
This tutorial will cover how to fix the requests dependency warning error while importing the Elasticsearch library for Python. There is a bug that sometimes throws a RequestsDependencyWarning error message when attempting to import the library for Elastic’s official Elasticsearch Python client. This error message is due to some versions of the Elasticsearch client requiring older versions of the urllib3 library, dating back to 2017. While the warning can be ignored, and even with the warning the Python API calls to Elasticsearch should continue to work properly, this article will explain two ways of avoiding the warning. The complete RequestsDependencyWarning in Elasticsearch with Python warning message is as follows:
1 | /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/requests/__init__.py:80: RequestsDependencyWarning: urllib3 (1.25.3) or chardet (3.0.4) doesn't match a supported version! |
Even though it lists both the urllib3 and chardet packages as being the potential problem, it is usually the Urllib3 that is causing the problem. The PIP requests’ __init__.py script, found in the python3/dist-packages/requests directory, permits for any version of chardet between 3.0 and 3.1.
Prerequisites for Connecting to Elasticsearch with the official Python Client
Python 3.x or greater should be used as Python 2.7 is now deprecated and will lose most of its support by 2020. Windows users can download the installer for Python3. Most Linux distros and macOS come with Python 3 already installed.
Elasticsearch must be installed and running on the same server making the Python API calls to the Elasticsearch cluster. Execute the following cURL request to confirm the cluster is running on the default port of
9200:
1 | curl -XGET localhost:9200 |
- The PIP package manager for Python 3 must be installed on the Elasticsearch cluster’s server. Execute the following command to check if
pip3has been installed correctly:
1 | pip3 --version |
The response should resemble the following:
1 | pip 19.1.1 from /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/pip (python 3.6) |
How to Obtain the PIP Packages Directory Location for Python 3
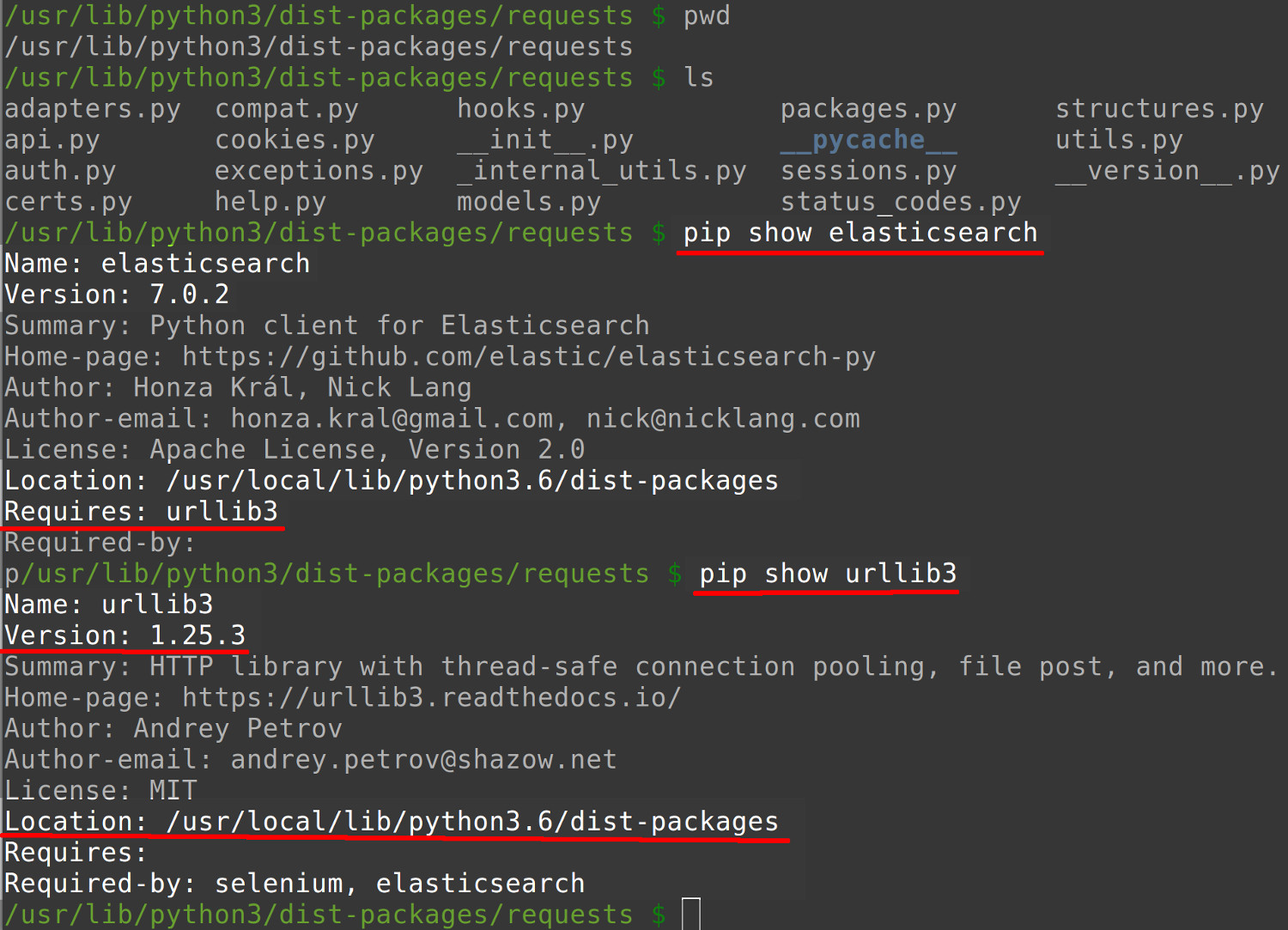
The __init__.py Python script that asserts compatibility for specific package versions should be located in the same directory returned by the pip3 --version command. As shown below, the pip show command can also be used to obtain information about the PIP installation and its location.
NOTE: This is the one exception for using pip instead of pip3 for Python 3.
How to Diagnose the RequestsDependencyWarning returned by Python
Open a terminal window and type python3 to access the Python 3 interactive interpreter. Once inside the shell, see if Python will return the RequestsDependencyWarning when attempting the following command to import the Elasticsearch client:
1 | from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch |
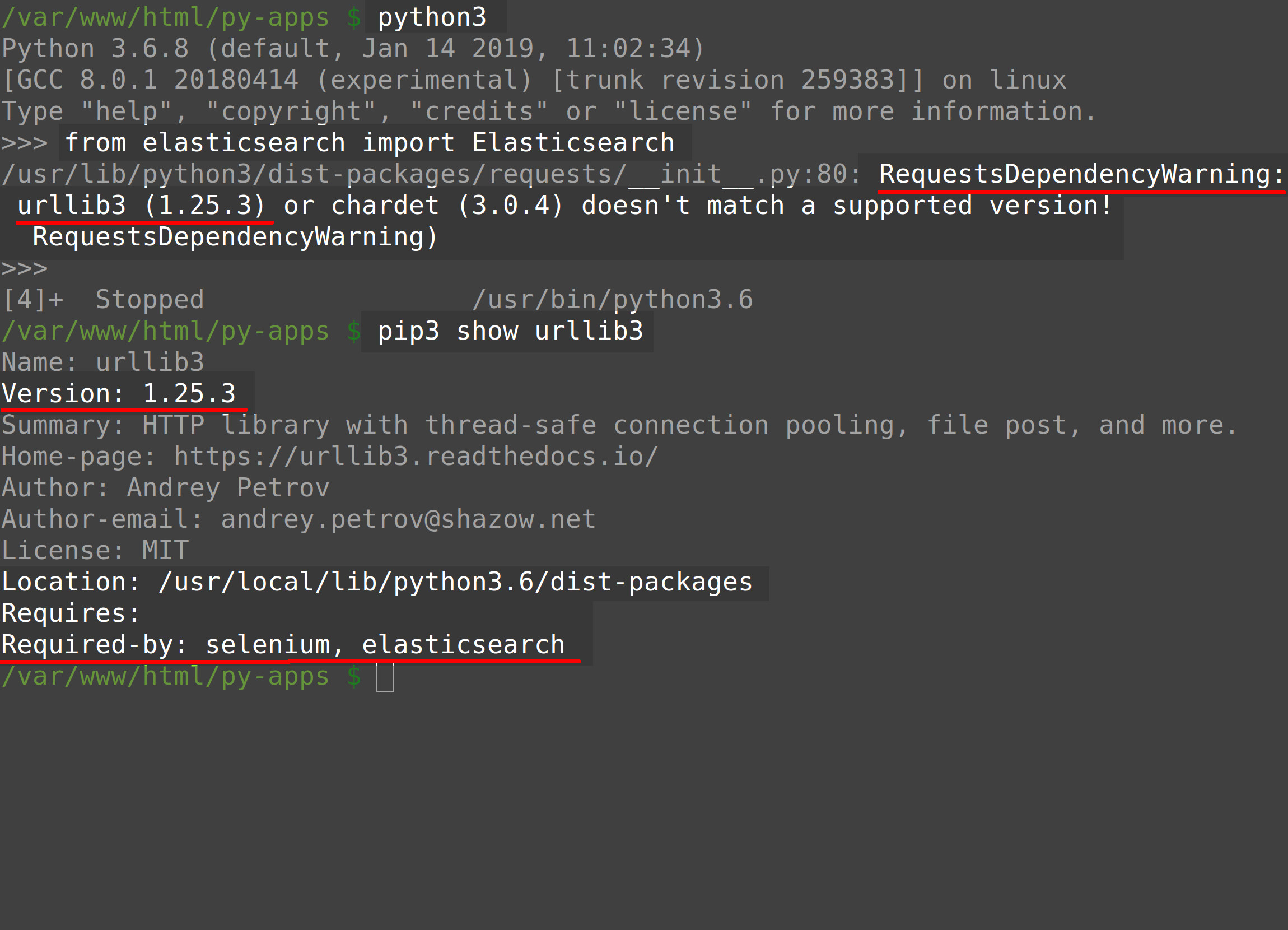
Now type exit() or press CTRL + Z to exit the interpreter.
Receiving the RequestsDependencyWarning when importing Elasticsearch in Python’s IDLE
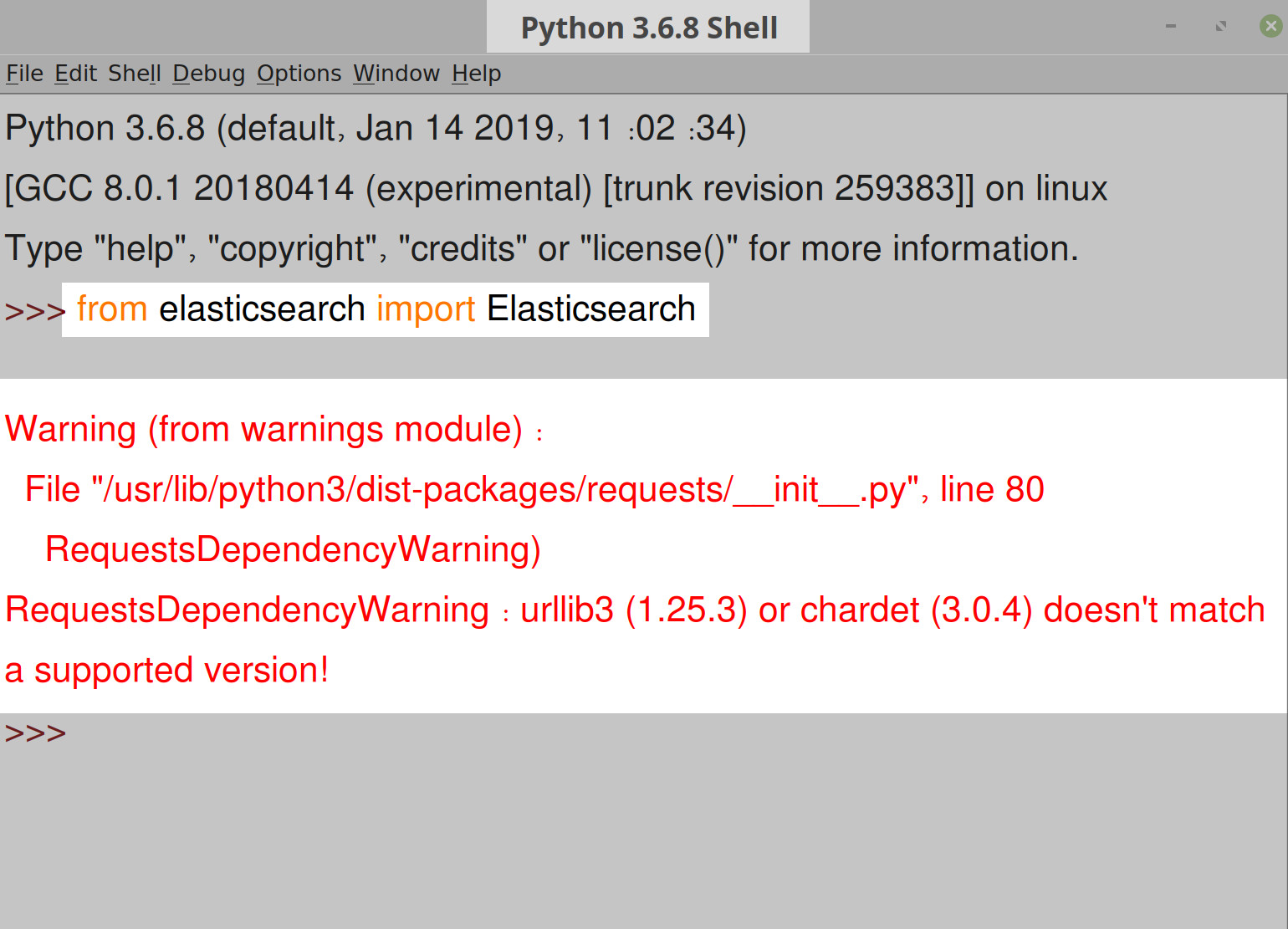
Another method for checking for the RequestsDependencyWarning warning in the IDLE integrated development environment for Python. Type idle3 in a terminal window to use Python 3, rather than version 2.7, and then type the following command into the text prompt:
1 | from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch |
The results should resemble the following:
Understanding the Error Message: PIP requires an older version of urllib3 from 2017
The source of the error problem results from Python’s requests library requiring an older version of urllib3, dating back to July 2017, shown in the following image:
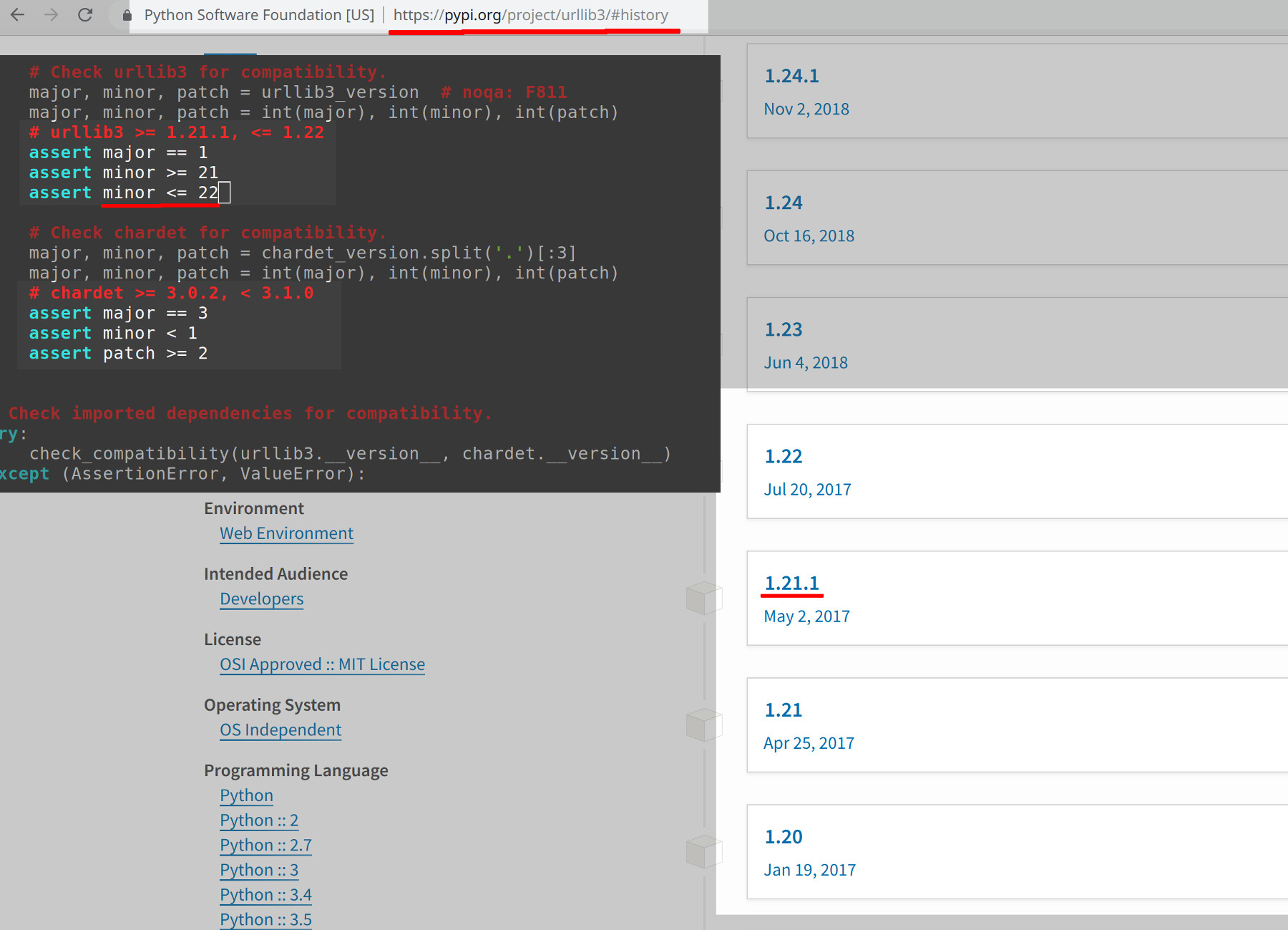
Navigate to the urllib3 page on the pypi.org website to get more information on the urllib3 package version.
Method One of Avoiding the Warning: Change the Requirements for the urllib3 Package’s Version Number
Change to the directory of the PIP3 package location. On a macOS HomeBrew installation of Python 3 this may be in the /usr/local/Cellar/ directory. Execute the which pip3 command to verify the current installation location and version of PIP.
How to change into the PIP library’s “requests” directory
Execute the following command:
1 | cd /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages/requests |
How to edit the requests directory’s ‘init’ script
Use a text editor, such as nano or gedit, to edit the __init__.py Python script in the requests directory with the following command:
1 | sudo nano __init__.py |
Execute the following command to change the line under the urllib3 settings that say assert minor so that it accepts versions less than or equal to 25:
1 | assert minor -= 25 |
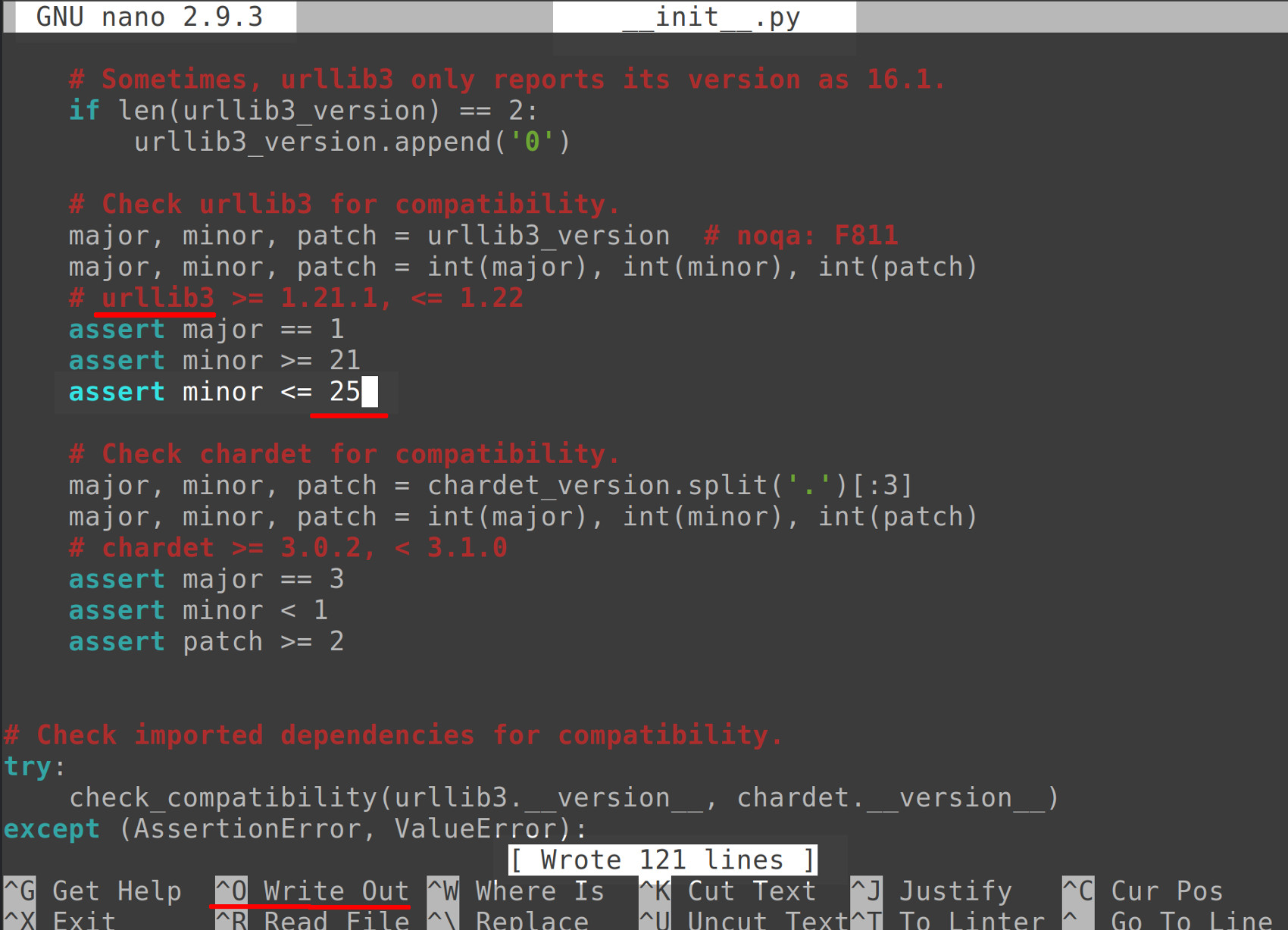
NOTE: Elevated sudo privileges may be required to modify any documents in this directory.
If nano was used to edit the file, press CTRL + O to write changes to the file and then CTRL + X to exit the editor.
Method Two of Avoiding the Warning: Install an Older Version of the urllib3 Package for Python
Execute the pip3 install command to install an older version of the urllib3 package in lieu of modifying the PIP3 __init__.py file.
Type the following command in a terminal window to install version 1.21.1 of the urllib3 package:
1 | pip3 install urllib3==1.21.1 |
This command will cause PIP to uninstall the newer version of urllib3 and install the older version from 2017. This should put a stop to receiving the import warnings.
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated two methods of fixing the requests dependency-warning error while importing the Elasticsearch library for Python. Remember that Elasticsearch API calls and requests can still be made successfully with the warning present or when using an older version of urllib3. Both of the methods covered in this tutorial are completely reversible if any issues with the RequestsDependencyWarning in Elasticsearch with Python occurs after executing these procedures. Just execute the -U command, shown below, to undo the changes and return urllib3 back to the last-used version:
1 | pip3 install urllib3 -U |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started



