Run Redis in a Docker Container
Introduction to Redis and Docker
The Docker engine compliments Remote Dictionary Server (Redis) by giving developers a dependable Redis Docker Engine strategy to run an instance of the Redis data structure as a service or as a compartmentalized container. Downloading the Bitnami Redis image from the Docker hub has many advantages. For one, changes from the upstream source are published instantly. Secondly, Bitnami provides the latest features and bug fixes fast, and project flexibility is enhanced because the configuration technique and elements are alike for the cloud images, containers, and virtual servers.
Prerequisites to running Redis with Docker
- Download and install PostgresSQL for your OS.
Install or run the Redis CLI library
- Install the Redis CLI package for your OS. OR
- Perform a container restart and run both Redis image and the Redis CLI image.
NOTE: If you use a macOS and installed Redis with Homebrew, the Redis CLI package should be included.
Install the Docker Engine
Get the Docker Engine on your OS or put it on your server. You’ll need to install it prior to running the container Redis.
Install Docker on Windows or macOS
Open an account with Docker so you can make a user profile.
Login, and then download the Docker installer.
Open the macOS DMG installer and follow the prompts to finish the installation.
Install Docker on macOS using Homebrew
- With Homebrew, you can bypass having a Docker account and do a Docker Engine installation. Use the command
brew install:
1 | brew install docker |
- Another option is to get the application Docker Machine with this command:
1 | brew install docker-machine |
- Perform a virtual box installation using this install command:
1 | brew cask install virtualbox |
Install ‘Docker CE’ on Linux
- Perform a Docker dependency package installation:
1 | sudo apt-get -y install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common |
Obtain the most recent Docker version with the command
sudo apt-get update.If you’re uncertain about the Linux version you have or the type of Distro running, use with the command
cat /etc/os-release.
NOTE: For CentOS and Fedora Linux Red Hat distros, use the command
yumto install the latest version with the YUM package manager.
- Get the Docker Packages GPG key. Use the command below for Ubuntu and Linux Mint distros that are Debian-based:
1 | curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add - |
- Obtain the Docker repository file
.debwith this command:
1 | sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release; echo "$UBUNTU_CODENAME") stable" |
Inspect the updated repository list with the command
cat /etc/apt/sources.list.d/additional-repositories.list:Next, perform another index update with the command
sudo apt-get update:Finally, accomplish a Docker Compose and Docker CE installation:
1 | sudo apt-get -y install docker-ce docker-compose |
Verify that the Docker Engine is running
Acquire a list of every image that was downloaded in the repository with the command
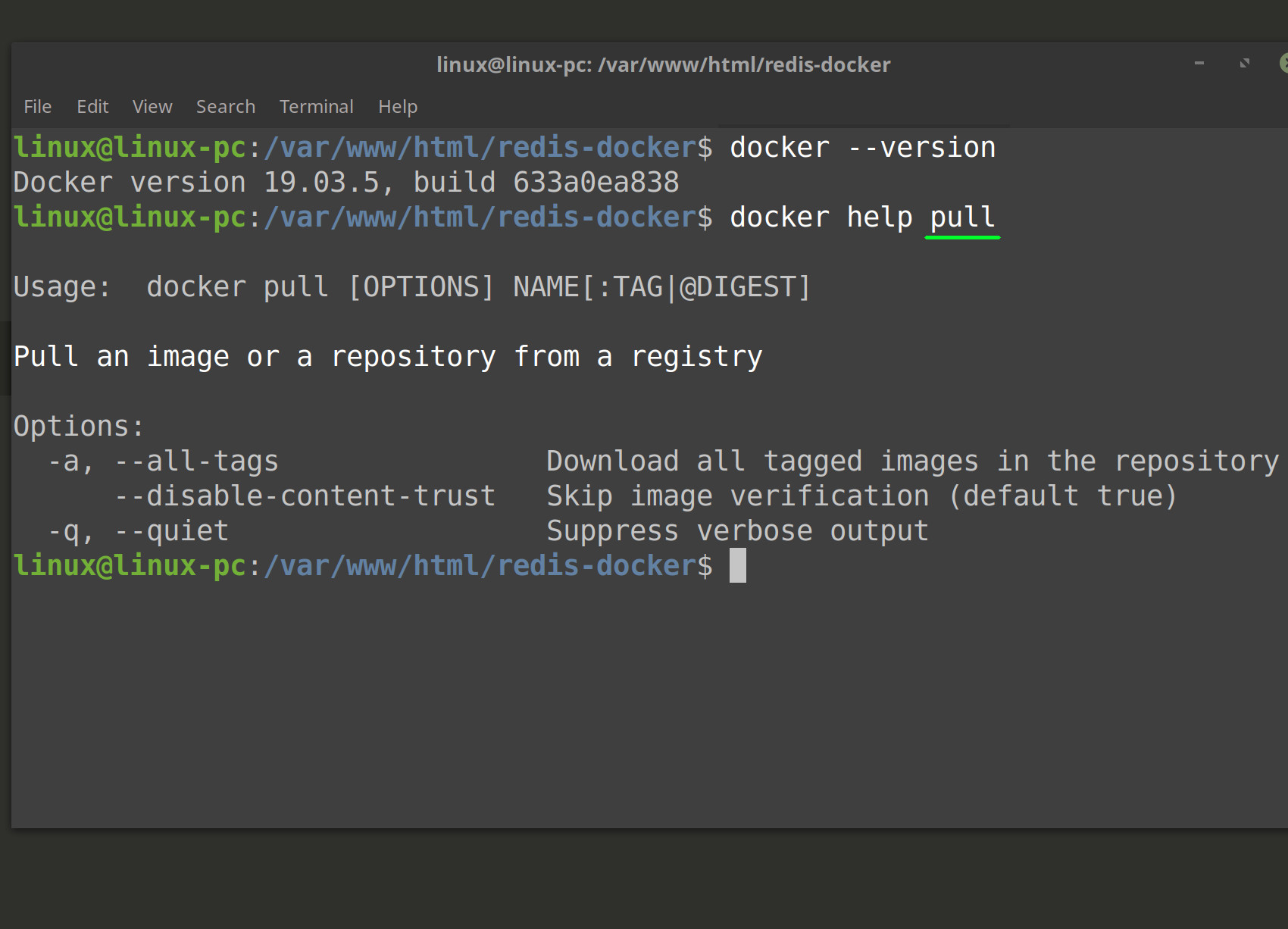
docker ps.To take a look at the details about various commands and Docker Hub features, input the command
docker helpalong with the topic you want to know more about. For instance, the commanddocker help pullreturns options that go along with that specific command as well as provide general information about image pulling.
NOTE: Get the version number of Docker with the command
docker --version.
Pull the Redis Docker image
- At Bitnami’s Docker image for Redis, you can complete a stable version Redis Docker image pull; otherwise, use this command:
1 | docker pull bitnami/redis |
NOTE: A default is available by using
docker pull redis.
List all of the Docker images
- Use this
lscommand along with--allor-ato view a list of every image from the repository:
1 | docker image ls -a |
NOTE: Hidden images will be included in the list because you added the flag
--allor-a.
Run the Redis Docker image
- Here’s an example where a container named
objrock-redisand thebitnami/redis(Redis image) that is being run as.
1 | docker run --name "objrock-redis" -d bitnami/redis |
NOTE: The mode “detached” is represented by the option
-d. The above command enables you to perform a detached mode launching of the container. Verify that you havesudopermissions if you experience issues starting the container in detached mode.
List the Docker containers to look for Redis
- Confirm that the container is active with the command
docker ps. If you don’t see container activity, use the-aflag or--allto include hidden containers:
1 | docker ps -a |
NOTE: Get even more specifics about a container with the command
docker logsand then list the container’s name.
- The output of your Docker container where you have the Redis image running should look something like this from a terminal window:
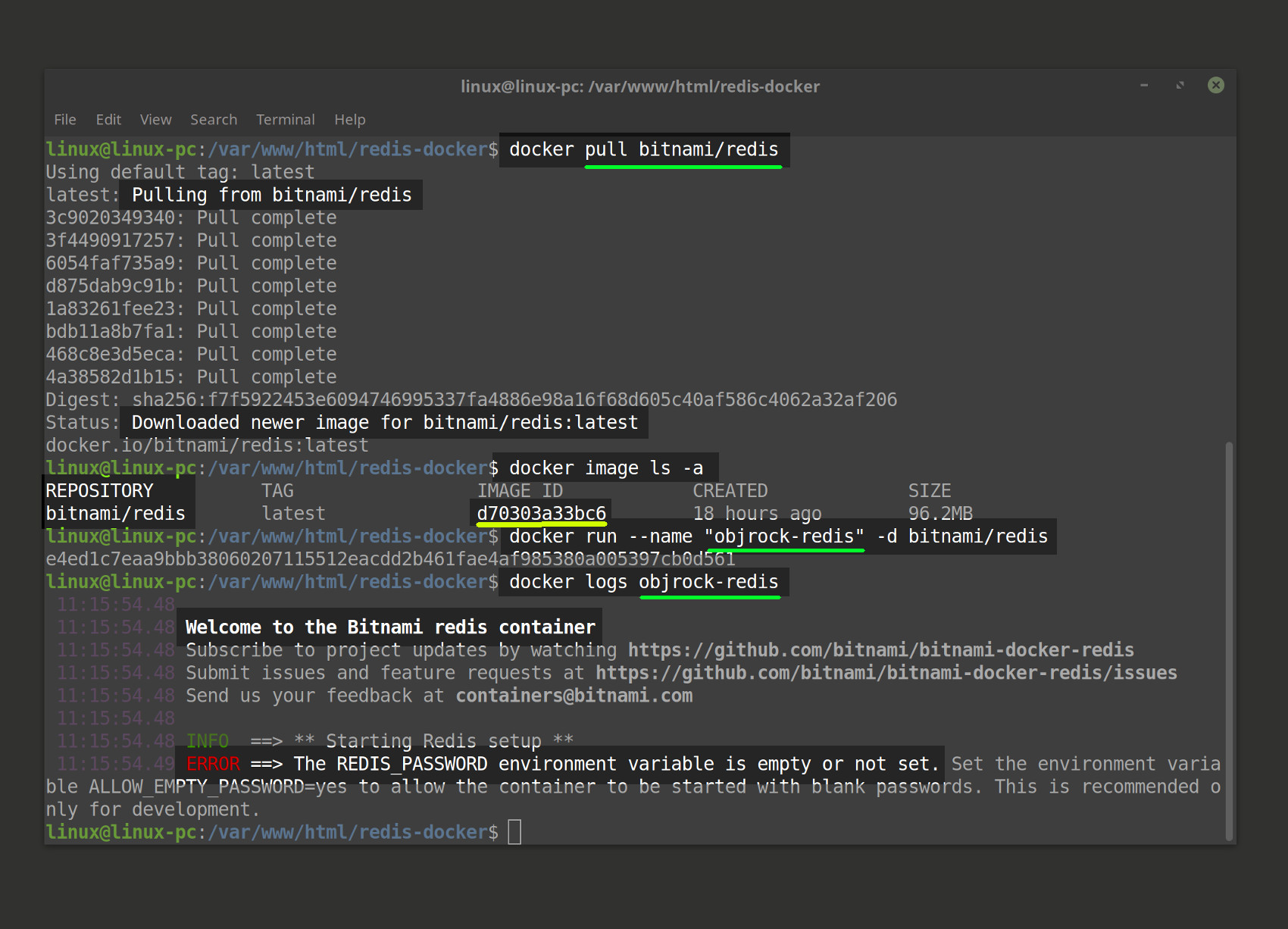
NOTE: Each container and Docker image has it’s own one-of-a-kind ID, so you’ll be able to tell it apart from any other container or image.
Setting a password for the Redis environment
You can set a password for your container. You should already have one set for your configuration for Redis. To apply a container password, identify it within the Docker environment file docker-compose.yml.
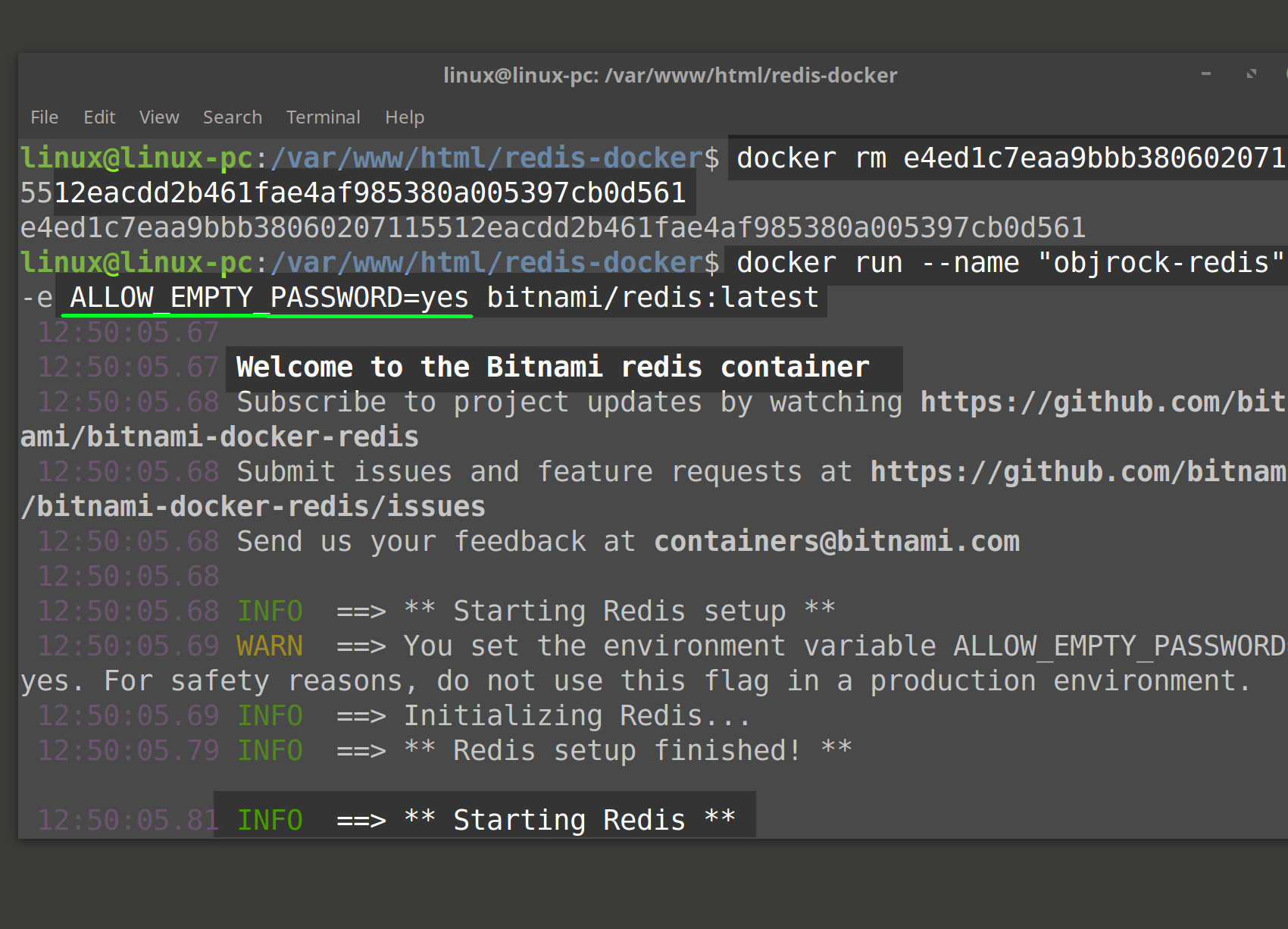
Run the Redis container without a password
- You can also run your container and skip assigning a password altogether so that it will not respond with the exception
REDIS_PASSWORD environment variable is empty or not set. Use theALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORDand-eflag like this:
1 | docker run --name "objrock-redis" -e ALLOW_EMPTY_PASSWORD=yes bitnami/redis:latest |
Another way to run the Redis image in a Docker container is by using command redis-cli, the Redis CLI image. First, check that the app Redis CLI is active. Verify that its configuration is correct as well. When finished with your confirmation checks, it’s okay to do your Redis port (default port 6379) container binding.
Conclusion to Redis and Docker
The convenience of using the Docker Engine to pull the Redis image and run the Redis data structure as a container is speed, agility, and project pliability. What’s more, viewing lists of every container along with their details helps manage your work. Organize, visualize, strategize. Try the Redis Docker way today!
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started




