Backing Up All Databases In PostgreSQL
Introduction
Backing up a database is one of the most critically important tasks in any type of database administration. Regular backups ensure that any data lost due to corruption, crashes and breaches can be successfully recovered. This tutorial will explain how implement the PostgreSQL builtin tools and administrative options used to back up all database in PostgreSQL.
Prerequisites to Back Up All Database in PostgreSQL
- The PostgreSQL server must be properly installed, configured and running.
Download PostgreSQL for Linux and Windows systems here
How to use the PostgreSQL pg_dump Command
The pg_dump command must be run in the terminal of the computer where the database is installed and in the command line on the computer where the database is stored.
The following code is used to back up a PostgreSQL database:
1 | pg_dump -U dbusername -W -F t dbname > /desired/derictory/dump_file_name.tar |
How to use the PostgreSQL Backup Extension Format
Multiple formats or extensions may be used to store the PostgreSQL database backup. Examples include:
- The
.tarformat for tarball - The
.bakformat for compressed binary format - The
.sqlformat for plaintext dump
Understanding the Various PostgreSQL pg_admin Backup Options
The following options can also be used to furnish additional instructions when executing the pg_dump command:
- The
-Uoption will specify the specific user connecting to the PostgreSQL database.
The
-Woption requires the user to furnish the proper password when connecting to the PostgreSQL server.The
-Foption can be used by the backup file as explained in the above “PostgreSQL Backup Extension Format” section.
How to Backup a Single Database in PostgreSQL
With an understanding of how the pg_dump can aid in performing a database backup, this section will cover exactly how to use the pg_dump command to backup a database.
First, connect to the PostgreSQL database using the PostgreSQL psql interactive terminal program. Next, list the current PostgreSQL database in the system, in its entirety, by using PostgreSQL command \l.
Execute the following commands in the given sequence:
1 | psql postgres -U dev |
Now execute the \l command.
The results should resemble the following:
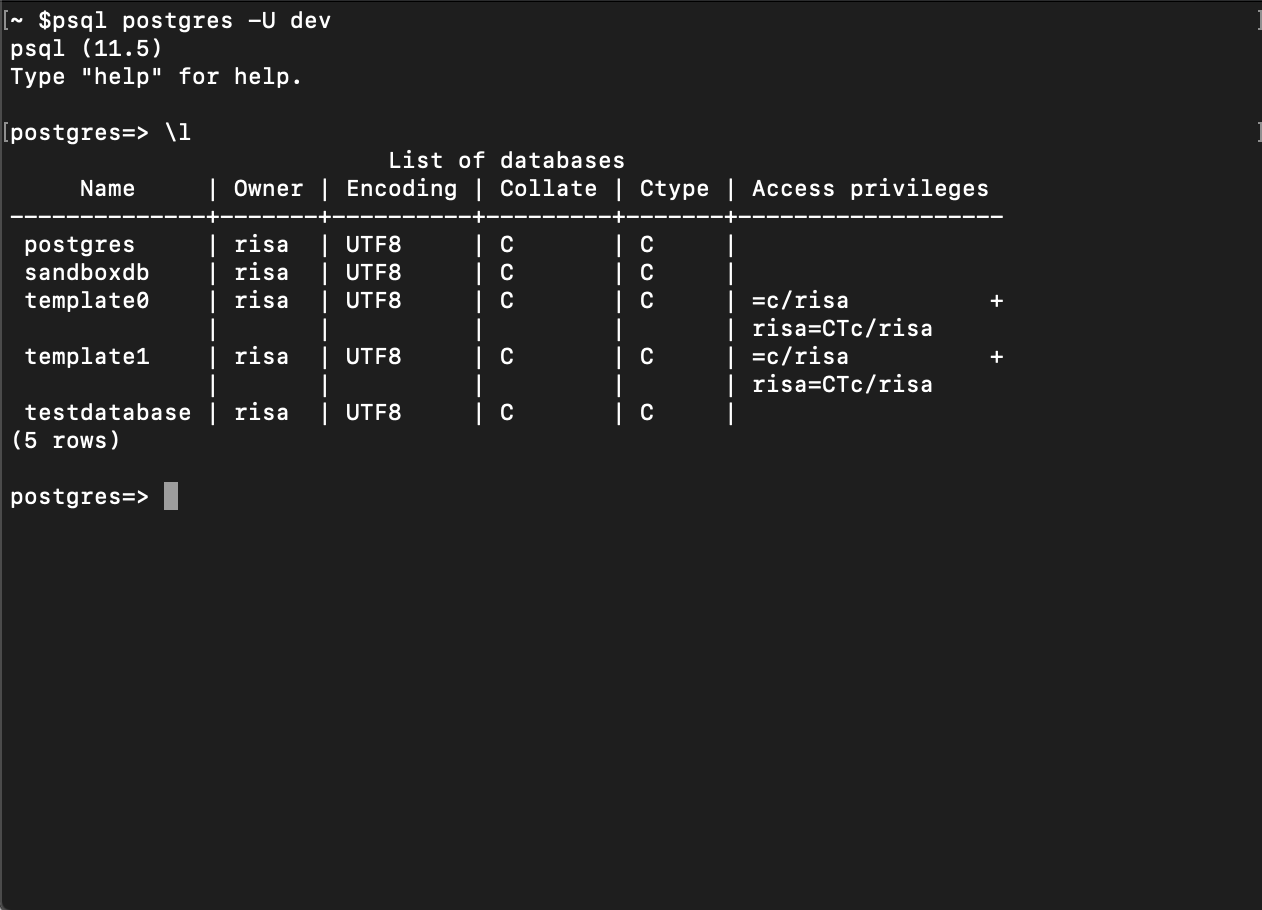
From here the decision on which database to back up can be made using the testdatabase command.
Now type the \q command to quit the database session and then execute the following code in the command line:
1 | pg_dump -U risa testdatabase > /Users/risa/documents/demo_single_backup.sql; |
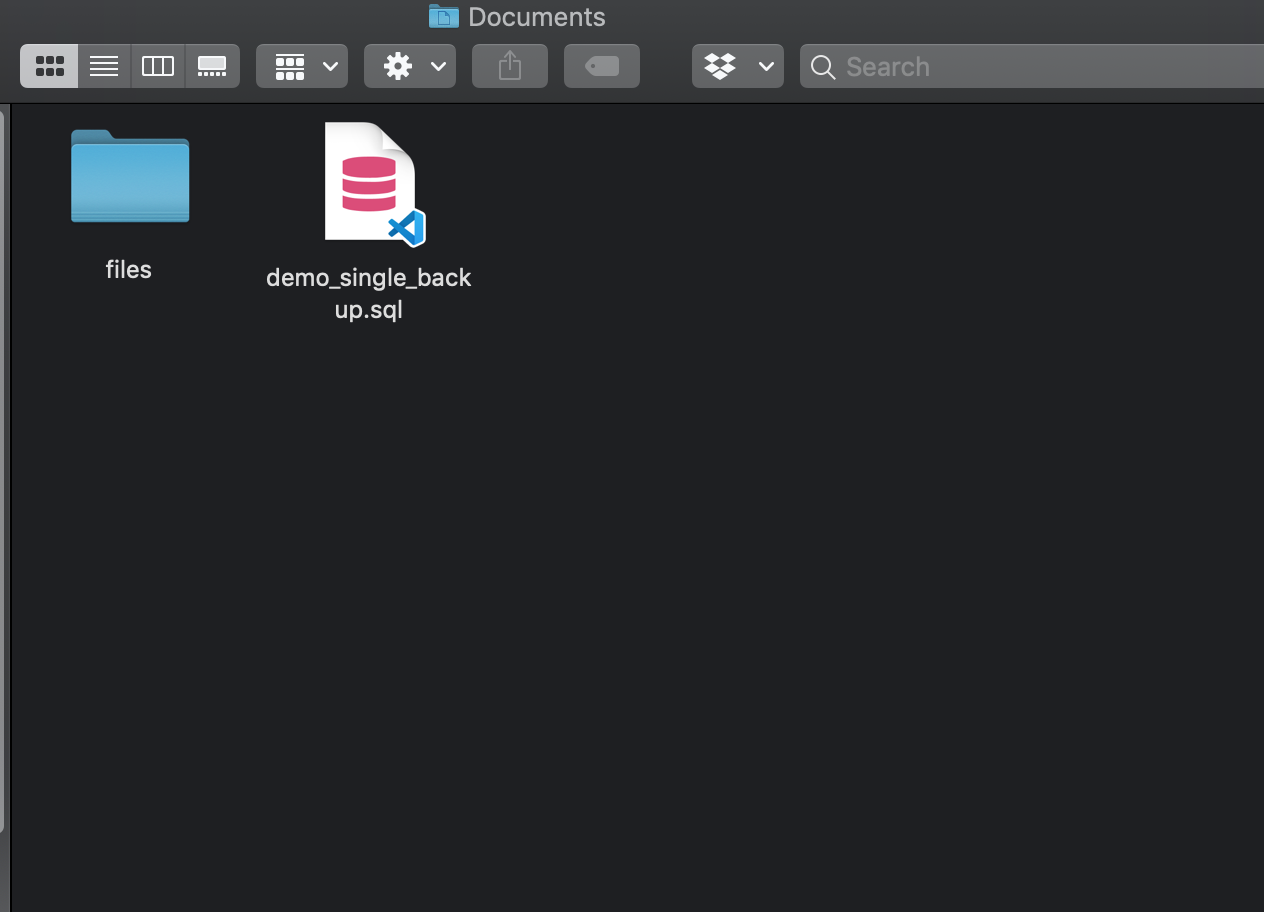
The above code instructs the pg_dump command to store the backup as the user risa in the following path: /Users/risa/documents/demo_single_backup.sql
The below image should be visible by navigating to the specified directory:
How to Backup All Database in PostgreSQL
The previous section covered how to backup a single PostgreSQL database. This section will explain how to backup all of the information existing in the database in PostgreSQL. This is accomplished by using the PostgreSQL pg_dumpall command to enable a backup of the entire database(s) at one time. However, note there are some caveats that should be taken into account before using this approach.
While it’s very convenient to be able to export all database at once, using a script file prohibits processing a parallel restore. The means that some of the processes will require more time than usual to execute a back performed in this manner.
In addition to the dumping of the database requiring more time, there is no way to determine what dump for which database is being performed while the process is ongoing.
The syntax for the pg_dumpall command is as follows:
1 | pg_dumpall -U username > /desired/derictory/dump_file_name.tar |
Now execute the below command to backup all of the existing database in PostgreSQL:
1 | pg_dump -U risa > /Users/risa/documents/demo_all_database_backup.sql; |
Notice that the syntax for both pg-dumpall and pg_dump is similar, but not identical. However, note that the -W option that instructs pg_dump to require a password was not used.
The following is the result of the pg_dumpall command:
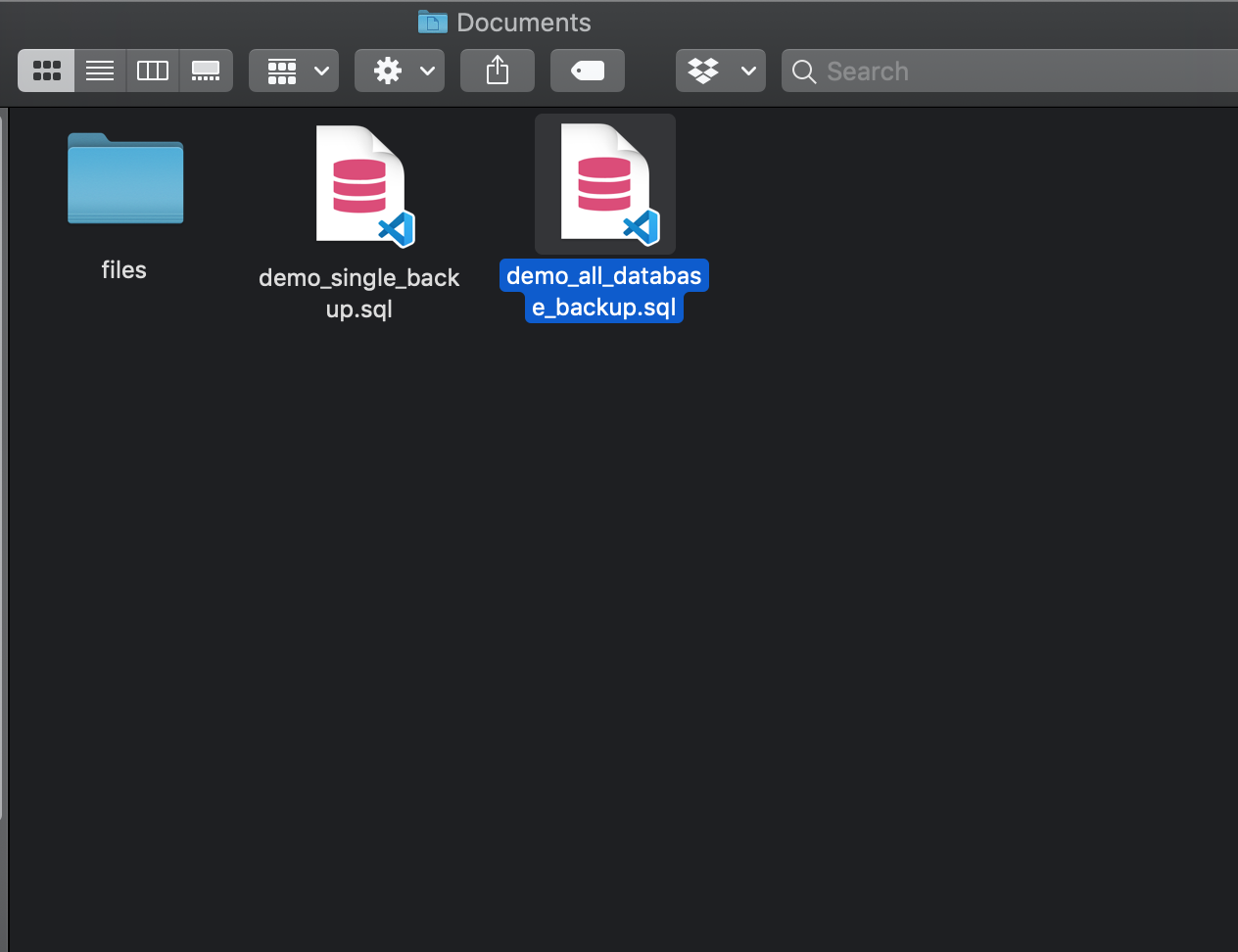
The above image compares the two files that were created in this tutorial, one for the single database backup and one for the multiple database backup.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to back up all database in PostgreSQL using the builtin PostgreSQL pg_dump and pg_dumpall tools. The article specifically covered how to use the PostgreSQL pg_dump command and use the PostgreSQL backup extension format. The tutorial also explained the PostgreSQL pg_admin backup options and how to backup both single and multiple databases in PostgreSQL. When performing backups, remember that the syntax for both pg-dumpall and pg_dump is similar, but not identical.
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started




