How to use Python to Encode a JSON File into MongoDB BSON Documents
Introduction
This tutorial will explain how to use Python to encode JSON files into MongoDB BSON documents using the BSON library. The library is useful for parsing JSON objects from files, strings, a Python dictionary or list and can also convert dictionaries and lists into JSON strings. As Python 2.7 has been deprecated, Python version 3 or later is recommend when performing the examples used in this tutorial.
Prerequisites for using Python to encode JSON file in MongoDB BSON documents
- Python must be properly installed and running. Python version 3 or later is recommend as Python 2.7 has been deprecated and scheduled to lose support.
How to install the PyMongo and BSON libraries using PIP3
Installing only pymongo is required, however, there is a stand-alone bson library as well. Install pymongo with the BSON library for Python 3 using the following pip3 command:
1 | pip3 install pymongo |
If there are version conflicts or import errors, uninstall the bson and pymongo libraries and then reinstall PyMongo with the included BSON package using the following commands:
NOTE: Use elevated sudo privileges in Linux
1 2 3 | sudo pip3 uninstall bson sudo pip3 uninstall pymongo sudo pip3 install pymongo |
How to use Python’s IDLE environment to test the BSON library
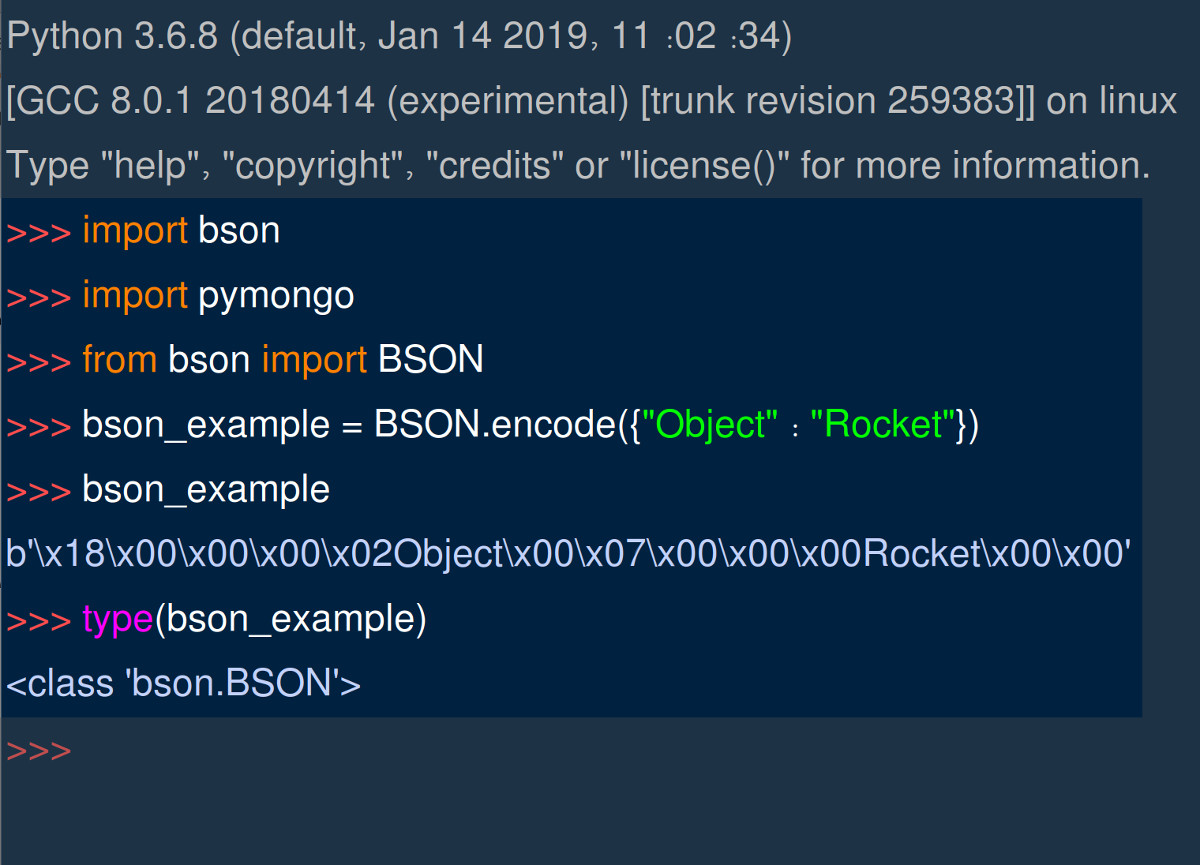
Execute the below commands in a Python interpreter, or use IDLE by typing idle3 or idle into a terminal or command prompt window, to test if the BSON library is properly installed and to confirm there are no version conflicts that will result in an ImportError:
1 2 3 4 | from bson import BSON bson_example = BSON.encode({"Object": "Rocket"}) print (bson_example) print (type(bson_example)) |
The results should resemble the following:
How to Create a JSON File with MongoDB Documents
Create a JSON file, with the .json file extension, and place some MongoDB documents into a JSON array enclosed in square brackets ([]) with the collection name as the array’s key.
Here are a few example documents to use:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | { "new hires": [ {"name": "Interpol Lundquist", "age": "50", "sex": "male", "accounts": "interpol_lundquist", "join_date": "2010-08-12 01:42:28"}, {"name": "Hebrides Adair", "age": "47", "sex": "male", "accounts": "hebrides_adair", "join_date": "2013-07-16 20:47:08"}, {"name": "Cantabrigian Gilchrist", "age": "21", "sex": "male", "accounts": "cantabrigian_gilchrist", "join_date": "2010-02-18 02:46:07"}, {"name": "Missy Chesapeake", "age": "42", "sex": "male", "accounts": "missy_chesapeake", "join_date": "2015-09-17 08:17:45"} ] } |
To use these documents, copy and paste the entire JSON object into a text file and save it. Here the filename data.json is used.
How to Create a Python Script and Import the Necessary MongoDB BSON Package Libraries
Create a new Python script with the .py file extension, making sure to import the JSON and BSON libraries at the top of the script, by executing the following commands:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 #-*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import the built-in JSON library import json # import the BSON library from PyMongo's bson from bson import BSON |
How to use Python to load a JSON File of MongoDB Documents
The Python open() function allows for opening documents, such as text, CSV, or JSON files, and returns the data as a _io.TextIOWrapper object that can be iterated over and parsed. Here is an example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | # declare an empty string object json_string = "" # use Python's open() function to load a JSON file with open("data.json", 'r', encoding='utf-8') as json_data: print ("data.json TYPE:", type(json_data)) # iterate over the _io.TextIOWrapper returned by open() using enumerate() for i, line in enumerate(json_data): # append the parsed IO string to the JSON string json_string += line |
NOTE: Make sure to pass the complete file path in the file name string if the JSON file is not in the same directory path as the Python script.
How to Validate the JSON String and Create a Python Dictionary from the MongoDB Documents
After the string is loaded into the Python script it must be converted into a valid JSON Python dict before the string can be encoded into a BSON object.
Understanding a ValueError exception example raised by json.loads()
The json.loads() method requires passing a valid JSON string to its method call. If the JSON string is not valid, then the JSON library will throw a ValueError exception.
The following script will execute a try-catch error indentation block to verify the JSON string is valid before attempting to encode it as a BSON object:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # here's an example of an invalid JSON string bad_json = '{"this is": "missing the closing bracket"' # json.loads() will throw a ValueError if JSON is invalid try: json.loads(bad_json) except ValueError as error: print ("json.loads() ValueError for BSON object:", error) |
Because the string is missing the closing bracket (}) for the JSON object to be complete, the above example will display the following message in the terminal window:
1 | json.loads() ValueError for BSON object: Expecting ',' delimiter: line 1 column 42 (char 41) |
How to pass the entire string of MongoDB documents to the json.loads() method
The json.loads() method should return a Python dict object consisting of the MongoDB documents, with the collection name as its key, provided the string was actually a valid JSON object:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | # make sure the string is a valid JSON object first try: # use json.loads() to validate the string and create JSON dict json_docs = json.loads(json_string) # loads() method returns a Python dict print ("json_docs TYPE:", type(json_docs)) # return a list of all of the JSON document keys print ("MongoDB collections:", list(json_docs.keys())) except ValueError as error: # quit the script if string is not a valid JSON print ("json.loads() ValueError for BSON object:", error) quit() |
How to Iterate the MongoDB Collection Names and JSON Documents
Once the JSON dictionary has been declared its collection keys can be iterated over, and subsequently each collection’s documents. This will convert the documents to BSON objects and vice versa. An example follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # iterate the json_docs dict keys (use iteritems() for Python 2.7) for key, val in json_docs.items(): # iterate each JSON document in the list for i, doc in enumerate(json_docs[key]): # bytearray([source[, encoding[, errors]]]) |
How to Use the BSON Library to Encode and Decode the JSON MongoDB Documents
Use the bson library’s BSON.encode() method to convert the dictionary value representing the MongoDB documents into BSON objects. The following example will execute another try-except block while decoding and encoding the JSON objects:
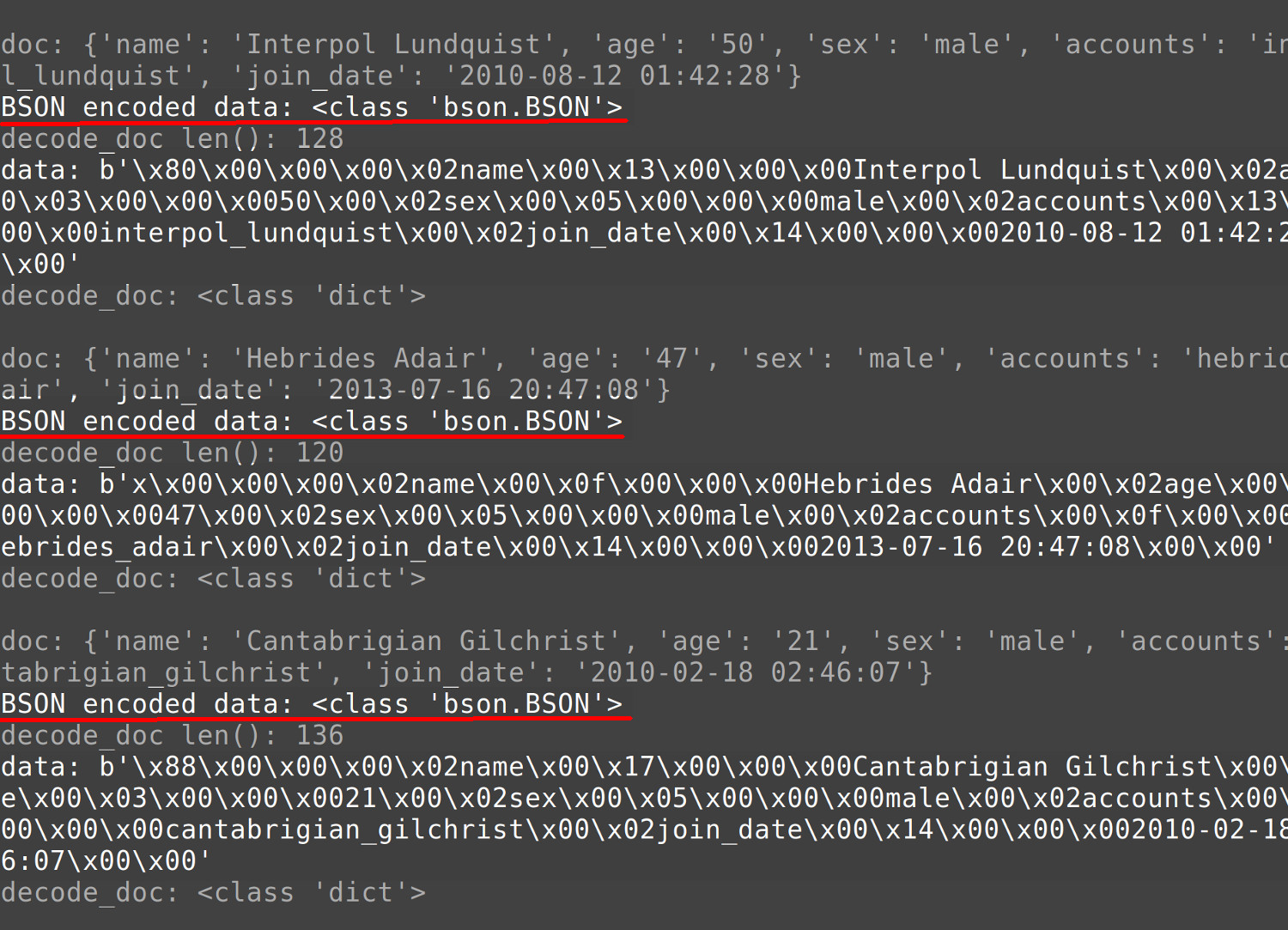
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | try: # print the original JSON document print ("\ndoc:", doc) # encode the document using the BSON library data = BSON.encode(doc) print ("BSON encoded data:", type(data)) # print the result of the BSON encoding print ("data:", data) # decode the BSON document back to a Python dict object decode_doc = BSON.decode(data) print ("decode_doc:", type(decode_doc)) except Exception as error: # catch any BSON encoding or decoding errors print ("enumerate() JSON documents ERROR:", error) |
Likewise, the BSON object can also be decoded back to a Python dict by passing the bson.BSON to theBSON.decode() method call.
The encoded BSON documents can then be inserted into a collection or used to make other API calls. The BSON format is a great way to parse MongoDB documents and is much faster than iterating JSON documents, as the former allows for skipping over unimportant MongoDB fields.
Here is a screenshot of a Python script printing the results of BSON encoded JSON documents:
Conclusion
This tutorial covered how to use Python to encode JSON files into MongoDB BSON documents. The article explained how to install the PyMongo and BSON libraries using PIP3, how to use Python’s IDLE environment to test the BSON library, how to use Python to load a JSON file of MongoDB documents, validate the JSON string, create a Python dictionary and how to iterate the MongoDB collection names and JSON documents. The tutorial also explained how to use the BSON library to encode and decode the JSON MongoDB documents and pass the entire string of MongoDB documents to the json.loads() method. Remember that after loading a string into the Python script it must be converted into a valid JSON Python dict before the string can be encoded into a BSON object.
Just the Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 #-*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import the built-in JSON library import json # import the BSON library from PyMongo's bson from bson import BSON # here's an example of an invalid JSON string bad_json = '{"this is": "missing the closing bracket"' # json.loads() will throw a ValueError if JSON is invalid try: json.loads(bad_json) except ValueError as error: print ("json.loads() ValueError for BSON object:", error) # declare an empty string object json_string = "" # use Python's open() function to load a JSON file with open("data.json", 'r', encoding='utf-8') as json_data: print ("data.json TYPE:", type(json_data)) # iterate over the _io.TextIOWrapper returned by open() using enumerate() for i, line in enumerate(json_data): # append the parsed IO string to the JSON string json_string += line # make sure the string is a valid JSON object first try: # use json.loads() to validate the string and create JSON dict json_docs = json.loads(json_string) # loads() method returns a Python dict print ("json_docs TYPE:", type(json_docs)) # return a list of all of the JSON document keys print ("MongoDB collections:", list(json_docs.keys())) except ValueError as error: # quit the script if string is not a valid JSON print ("json.loads() ValueError for BSON object:", error) quit() # iterate the json_docs dict keys (use iteritems() for Python 2.7) for key, val in json_docs.items(): # iterate each JSON document in the list for i, doc in enumerate(json_docs[key]): # bytearray([source[, encoding[, errors]]]) try: # print the original JSON document print ("\ndoc:", doc) # encode the document using the BSON library data = BSON.encode(doc) print ("BSON encoded data:", type(data)) # print the result of the BSON encoding print ("data:", data) # decode the BSON document back to a Python dict object decode_doc = BSON.decode(data) print ("decode_doc:", type(decode_doc)) except Exception as error: # catch any BSON encoding or decoding errors print ("enumerate() JSON documents ERROR:", error) |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started



