How to Update a MongoDB Document Using the Golang Driver
Introduction
The tutorial will explain the UpdateOne() API method to update a document with the Mongo-go-driver using the official Golang driver for MongoDB. It will also show how to update a MongoDB document with its BSON _id. In order to update a MongoDB document with Golang, both software packages must be installed on the same machine.
Prerequisites for Creating a MongoDB Index in Golang
MongoDB must be properly installed and running. Enter
mongoto confirm the Mongo Shell is working properly.Golang must be properly installed on the same machine running MongoDB and the
$GOPATHdirectory for the Golang projects must be set.The official
mongo-go-driverGolang driver for MongoDB must be installed on the server or machine’s$GOPATHusing the following command:
1 | go get go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo |
- At least one document with data fields that can be updated must exist in a MongoDB collection.
How to Connect to MongoDB using a Golang Script
The API call must be done in a Golang script using the .go file extension. Create a folder or finder window, or use the touch command, in the terminal. Make sure to include package main at the top of the script.
How to import the required MongoDB and Golang packages
Use Golang’s import statement to import the Golang and MongoDB packages to update a document with the following command:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "os" "reflect" // get an object type // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) |
How to connect to MongoDB using the Golang driver’s options.Client() method
Declare the main() function where the data insertion and MongoDB insertOne() API call will take place by using the func keyword:
1 | func main() { |
How to connect to MongoDB in Golang
Declare a new options.Client() instance inside the main() function to create a new connection to MongoDB. Change the host and port URI settings to match the server’s domain and MongoDB settings with the following command:
1 2 3 | // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "\n") |
As shown below, pass the clientOptions instance to the mongo.Connect() method and make sure to pass a context.TODO() object to it:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { fmt.Println("mongo.Connect() ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } |
How to Declare a New MongoDB Collection Instance from a Database Using the Golang Driver
Use the following command to create a new MongoDB collection instance, making sure to pass the correct collection and database-string names to the methods:
1 2 3 | // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("some_database").Collection("Some Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "\n") |
How to Update a MongoDB Document by Looking Up its BSON _id
A document can be updated by creating a filter query by passing its _id as a BSON ObjectID to the UpdateOne method call.
How to instantiate an ObjectID from a MongoDB _id string
Declare a MongoDB ObjectID by passing a string of the document _id to the Primitive package’s ObjectIDFromHex() method:
1 2 3 | // Declare an _id string and create an ObjectID docID := "5d1719988f83df290e8c92ca" objID, err := primitive.ObjectIDFromHex(docID) |
How to check the ObjectIDFromHex() method for returned errors
Execute the following command to check for any returned errors:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Check for MongoDB ID ObjectIDFromHex errors if err != nil { fmt.Println("ObjectIDFromHex ERROR", err) } else { fmt.Println("ObjectIDFromHex:", objID) } |
Declare a nested BSON filter and pass the ObjectID instance to the inner bson.M
Declare another primitive.M array and nest the "$eq" operator, with the document’s ObjectID as its value, inside the outer bson.M object with the following comamnd:
1 2 | // Declare an _id filter to get a specific MongoDB document filter := bson.M{"_id": bson.M{"$eq": objID}} |
Notice how the _id filter is an extremely valuable tool for updating a specific document.
How to Declare a MongoDB Filter BSON Object in Golang
The UpdateOne() method will accept any filter query. If multiple documents have matching values, only the first matching value the API iteration encounters will be updated.
How to filter out a MongoDB document using a nested bson.M filter query
Following is an example of a MongoDB query filter spanning multiple lines of code that evaluates the documents’ boolean value for one of its fields:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Declare a BSON update object that will change a boolean field to 'false' filter := bson.M{ "fieldbool": bson.M{ "$eq": false, // check if bool field has value of 'false' }, } |
Note: A comma must be added at the end of the line of code for each closing bracket (}) so the system doesn’t return the “missing ',' before newline” error.
How to Declare a BSON Object for Updating MongoDB Fields
Execute the following command to declare a BSON object:
1 2 | // Declare a filter that will change a field's integer value to `42` update := bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"fieldint": 42}} |
How to update several fields in a MongoDB document using Golang
To allow for updating multiple fields for a document with the single API call, delimit each MongoDB document field-value pair using commas as shown here:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | // Create a nested BSON document for the documents' fields that are updated update := bson.M{ "$set": bson.M{ "fieldstr": "ObjectRocket UPDATED!!", "fieldbool": false, }, } |
How to Call the Golang Driver’s UpdateOne() Update Method for a MongoDB Document
Call the UpdateOne() method for MongoDB and pass a context object and the filter and update Primitive BSON objects to its method call with the following command:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Call the driver's UpdateOne() method and pass filter and update to it result, err := col.UpdateOne( context.Background(), filter, update, ) |
Now have the API return both a results and error object so each can be evaluated.
How to Check for Errors and the UpdateOne() API Results
The final step is to evaluate the err error variable and obtain the attributes of the results object as follows:
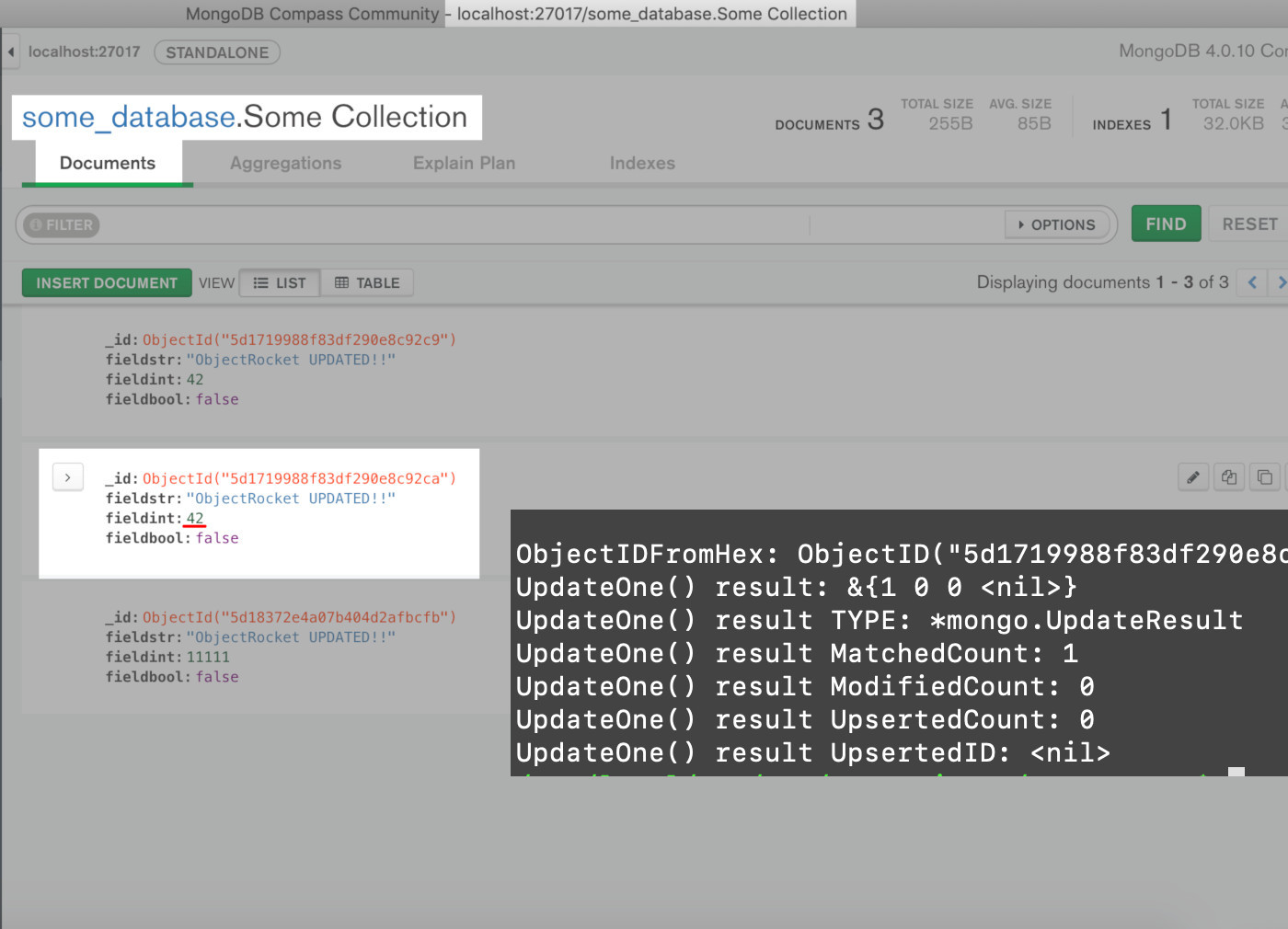
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | // Check for error, else print the UpdateOne() API call results if err != nil { fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } else { fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result:", result) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(result)) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result MatchedCount:", result.MatchedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result ModifiedCount:", result.ModifiedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result UpsertedCount:", result.UpsertedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result UpsertedID:", result.UpsertedID) } } |
Note the ModifiedCount integer value for the UpdateOne() results will always be either 0 or 1.
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated how to update a MongoDB document using the official Golang driver’s UpdateOne() API call. Specifically, this article explained how to connect to MongoDB using a Golang script, how to declare a new MongoDB collection instance, check for errors and filter out a MongoDB document using a nested bson.M filter query. Remember that in order to update a MongoDB document with Golang both the MongoDB and Golang software packages must be installed on the same machine. Also, to update a document with the Mongo-go-driver the official Golang driver for MongoDB must be installed on the server or machine’s $GOPATH.
Using MongoDB Compass UI to verify the document was successfully inserted with the Golang script
Just the Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "os" "reflect" // get an object type // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson/primitive" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) func main() { // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "\n") // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { fmt.Println("mongo.Connect() ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } // Declare Context type object for managing multiple API requests //ctx, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 15*time.Second) fmt.Println("context type:", reflect.TypeOf(context.Background()), "\n") // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("some_database").Collection("Some Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "\n") // Declare an _id string and create an ObjectID docID := "5d1719988f83df290e8c92ca" objID, err := primitive.ObjectIDFromHex(docID) // Check for MongoDB ID ObjectIDFromHex errors if err != nil { fmt.Println("ObjectIDFromHex ERROR", err) } else { fmt.Println("ObjectIDFromHex:", objID) } // Declare an _id filter to get a specific MongoDB document filter := bson.M{"_id": bson.M{"$eq": objID}} // Declare a BSON update object that will change a boolean field to 'false' /* filter := bson.M{ "fieldbool": bson.M{ "$eq": false, // check if bool field has value of 'false' }, } */ // Declare a filter that will change a field's integer value to `42` update := bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"fieldint": 42}} // Call the driver's UpdateOne() method and pass filter and update to it result, err := col.UpdateOne( context.Background(), filter, update, ) // Check for error, else print the UpdateOne() API call results if err != nil { fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } else { fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result:", result) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(result)) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result MatchedCount:", result.MatchedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result ModifiedCount:", result.ModifiedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result UpsertedCount:", result.UpsertedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateOne() result UpsertedID:", result.UpsertedID) } } |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started




