How to Install and Setup a MongoDB Server on MacOS
Introduction
One of the benefits of having a MongoDB server on your macOS is that it resembles a Unix-like system. That being said, you can do a lot with a Linux distro and MongoDB’s latest version. The best news is that you can use a variety of methods to install MongoDB on the different distros of Linux. So let’s proceed with this tutorial on how to install and setup a MongoDB server on macOS.
Prerequisites:
- Localhost web server – It must be running.
OR
- Linux server remote SSH access – You must have
sudoprivileges and a private key to gain access.
Debian-based distros: Install and Run MongoDB
Use the APT (Advanced Packaging Tool) repository manager to install and run the MongoDB server.
The
sources.list.dfile must have the MongoDB repository added to it.
1 | echo ""deb [ arch=amd64 ] https://repo.mongodb.org/apt/ubuntu bionic/mongodb-org/4.0 multiverse"" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/mongodb-org-4.0.list |
- Access a terminal in Linux before you add MongoDB or anything else that is new. Prepare your OS by updating all repositories.
1 | sudo apt-get update |
- Next, go ahead and install MongoDB. Include dependencies that go with it.
1 | sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org |
or specify a particular version
1 | sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-org=4.0.9 mongodb-org-server=4.0.9 mongodb-org-shell=4.0.9 mongodb-org-mongos=4.0.9 mongodb-org-tools=4.0.9 |
- If you experience problems locating
mongodb-org, try thesudo apt-get installmethod below:
1 | sudo apt-get install php-mongodb |
>NOTE: The repository file sources.list.d has to be complete and all packages have to be intact, nothing broken. If you come across an incomplete repository or some other error occurs, don’t stress. Just remove MongoDB entirely. Yes, it’s best to purge instead of trying to figure out the error because it could be anywhere and you don’t want to waste time. The sudo apt-get purge mongodb-org* command will get you to a place where you can start the installation process again.
Red Hat distros: Install and Run MongoDB
The YUM (Yellowdog Updater Modified) package manager works well with Red Hat Linux distros. Fedora and CentOS use YUM for installations. The good news is that within the directory of the YUM repository, a
.repofile for MongoDB is created.Use
cdto create the MongoDB repository.repofile.
1 | cd /etc/yum.repos.d/ |
The sudo command
touchcreates the.repofile. You’ll do this when you’re in theyum.repos.dfolder. Check that you downloaded MongoDB’s current installation because you want to base the.repofile on that.Next, the
nanocommand line editor allows you to do some file editing.
1 2 3 | sudo touch mongodb-org-4.0.repo sudo nano mongodb-org-4.0.repo |
- Edit the file by pasting the repository installation’s configuration settings information.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | [mongodb-org-4.0] name=MongoDB Repository baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/4.0/x86_64/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc |
- Now that the YUM directory contains the
.repofile, you’re ready to install MongoDB.
1 | sudo yum install mongodb-org |
Update repositories with the
YUMcommand This is the simplest way for those that use the RPM (Red Hat Package Manager):CentOS distros
Fedora distros
Red Hat distros
1 2 3 4 5 | sudo yum update # use 'upgrade' to install the updated packages: sudo yum upgrade |
Use PHP and PEAR: Install and Run MongoDB
The PHP Extension and Application Repository is another way to install MongoDB. Before you begin though, use php --version to verify your current version of PHP on your OS.
1 2 3 | php -v php --version |
- Check that your PHP 7 version is complete. Verify that you have the necessary development libraries for it.
1 2 3 | # replace `7.x` with your version of PHP 7 sudo apt-get install php7.x-dev |
- PEAR has a
pecllibrary. Install MongoDB with it.
1 | sudo pecl install mongodb |
The version is identified on a macOS terminal by using the pear version command.
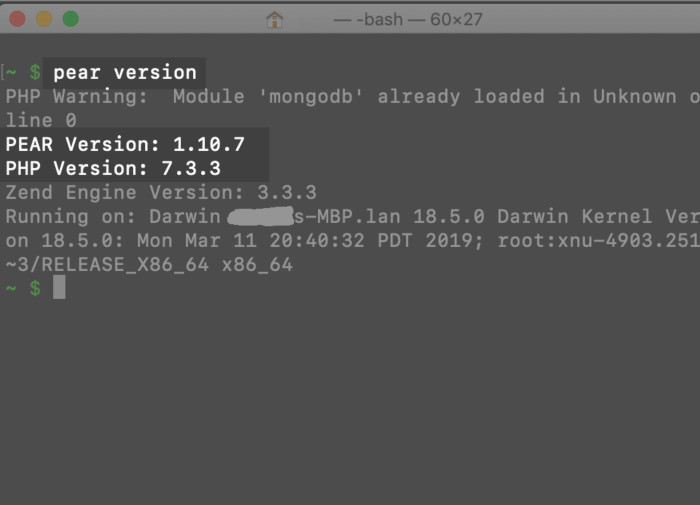
Be sure to verify your installation of PEAR .
Use a Tarball archive: Install and Run MongoDB
- You can install and run MongoDB using a tarball archive. After you download, you can unarchive it.
Use cURL to download Tarball file
1 | sudo curl -O https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.9.tgz |
Use tar to unpack the Tarbarll file
1 | sudo tar -zxvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.9.tgz |
A new directory will contain the unpacked installation files for MongoDB.
Move it to the
$PATHenvironment variable
OR
- Link it symbolically to point to the directory folder
Option 1: MongoDB Directory – Use MV for Path Exporting
The
mvcommand will move the MongoDB archive (unzipped) to a new location where it can stay for good.If you do that, the next thing you’ll want to do is use
cdto gain access into the directory.The
pwdcommand will show you the directory’s path.For the ability to gain access to the folder wherever, export the directory’s name and its path to
$PATHin Linux.
1 | export PATH=/some/path/mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.9/bin:$PATH |
- Another way to export the path is to copy and paste the following code below in the
~/.bashrcfile:
1 | export PATH=$PATH:/some/path/mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.9 |
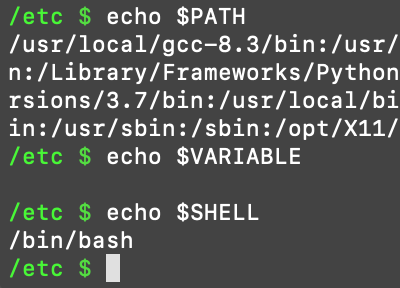
To look at every environmental path, use the
echo $PATHcommand.To view every environmental variable, use the
echo $VARIABLEcommand.
Option 2: MongoDB Directory – Move it to Linux
For this option, there are two ways to move the MongoDB directory:
- Put it in a system directory of Linux
OR
Put it in an established environment in Linux such as:
/usr/bin/usr/local/bin- another similar path based on your OS and Linux system
1 | sudo cp .... |
- View the environment path directory listing by inputting the terminal command:
echo $PATH
Optional Validation Task: Use a Public Key
- If you want to validate the installer’s character, you can download a GPG public key and the TAR archive at the same time. Start with this script:
1 | sudo curl -LO https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-4.0.9.tgz.sig |
- To get the public signature file, use
cURL.
1 | sudo curl -LO https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.0.asc |
- The last step in this process is to use
cURLagain to import the server.
1 2 | curl -LO https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-3.4.asc gpg --import server-3.4.asc |
Use Composer: Install and Run MongoDB
- You can use composer to install MongoDB as well through composer require mongodb/mongodb.
MongoDB: Setup and Configure the Server
- If you don’t see the file
mongodb.servicein thecd /etc/systemd/system/system directory, then in the terminal, paste the following code:
1 | /etc/systemd/system/mongodb.service |
It’s likely that you won’t find MongoDB files in the
systemfolder, but you can tryls -Ato find out after you accessed thesystemfolder.Go to the directory
/etc/systemd/system/and use the commandtouchto create themongodb.servicefile.
1 | sudo touch mongodb.service |
- Edit the
mongodb.servicefile you just created with the command line terminal editornanoor another one.
1 | sudo nano mongodb.service |
Export the file’s changes you just made by pressing Ctrl+O
Next, close the command line terminal editor
nanoor whichever one you used to edit by pressing Ctrl+X.Press CTRL+O to output the changes to the file, and then press CTRL+X to close the
nanoeditor running in terminal.Try these sudo commands:
sudo systemctl start mongodb
- sudo systemctl status mongodb
NOTE: To stop MongoDB service in Linux while in the terminal, press Ctrl+Z.
MongoDB: Test it. Start it up
1 | mongod --port 42424 |
Time to Create a MongoDB Database Directory
You might already have a directory for MongoDB. Find out by going into a terminal and pasting the data directory path
/data/db/. Press Return when finished.If you receive a “error: dbpath (/data/db) does not exist” or similar error message, create the
`/data/db/by entering the following code:
1 | sudo mkdir -p /data/db/ |
- Start up the MongoDB service
1 | sudo service mongod start |
*Restart the MongoDB service
1 | restart: sudo service mongod restart |
*Stop MongoDB service
1 | stop: sudo service mongod stop |
- Type Ctrl+Z to stop running the MongoDB service in the terminal.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained the various Linux distros and how you can setup MongoDB server on a macOS with them. Among the ways discussed, we talked about Debian-based, Red Hat, PHP and PEAR, Tarball archive, Composer, plus some more tips and tricks. With so many choices, you can select the method that suits you best.
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started


