How to Install and Setup a MongoDB Server on macOS
Introduction
MongoDB and macOS make a complementary duo. MongoDB is the perfect storage database for JSON documents. It offers scalability as well as flexibility for indexing and querying. Combine it with the power of macOS and you’ll unleash zooming productivity that will spoil you. Install MongoDB server macOS and there’s nothing stopping your search capabilities.
Setting up MongoDB on your macOS isn’t difficult if you have a streamlined way of getting it done. Two common ways to accomplish this are by using a Tarball archive from the MongoDB website or from the terminal with the Homebrew installer package. The latter is the simplest. If you go that route, be sure to install the brew package manager first. Let’s try both methods. This step-by-step tutorial explains how to install and setup a MondoDB on macOS.
Open a terminal instance
The macOS Dock might have the Terminal application anchored. If not, the “Applications” folder is where you want to open a terminal instance. Use the finder to do this.
Look for the “Utilities” folder, then open it and you’ll see the terminal application there.
The macOS finder shows an alphabetical listing of apps from left to right. Inside the Utilities folder is the Terminal.app. 
- Another way to install Homebrew is to run a Ruby script. If you haven’t installed Homebrew yet, use this code. The Git respository is where the Ruby script will run from to install the application.
1 | /usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl --insecure -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" |
Homebrew is downloaded and installed from a macOS terminal window .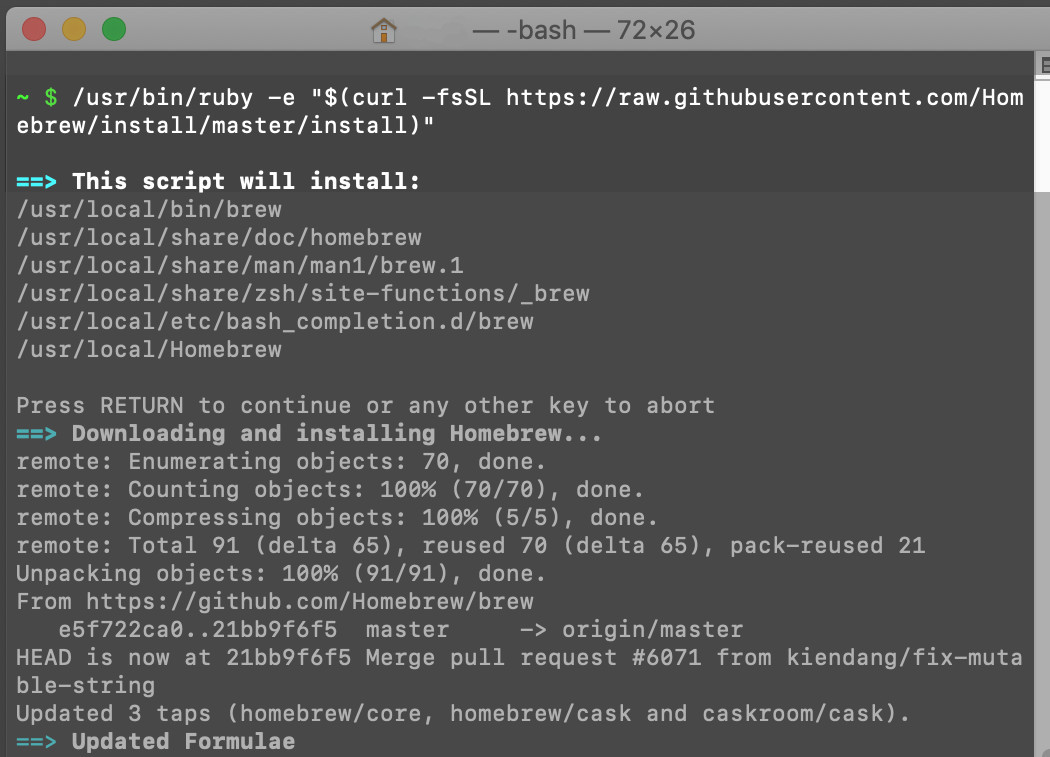
Use Homebrew to Install MongoDB
Now, you’re ready to install MongoDB. It’s best practice to update the brew packages first. You want the latest version because you want to take advantage of the latest technology.
1 | brew update |
- To install
brew, just “tap” the repository, that is to gain access to the repository after thebrewupdate is completed.
1 | brew tap mongodb/brew |
- The fast way to complete the tapped repository is to use the
installcommand. It’s also important to replace your MongoDB with the latest version.
1 2 | brew install mongodb-community@X.x # or: brew install mongodb-community@4.0 |
Use a terminal window to run MongoDB
- In a terminal window, start the MongoDB and run it as a service.
1 | mongod --config /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf |
Also in the terminal window, use nano or another command line editor to edit the configuration file found at /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf:
1 | sudo nano /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf |
Great! You’ve got the MongoDB Homebrew server running!
How to Stop the terminal service, MongoDB
- Press CTRL+C to stop the MongoDB community service and close the terminal window.
Stopping the MongoDB service in a macOS terminal. 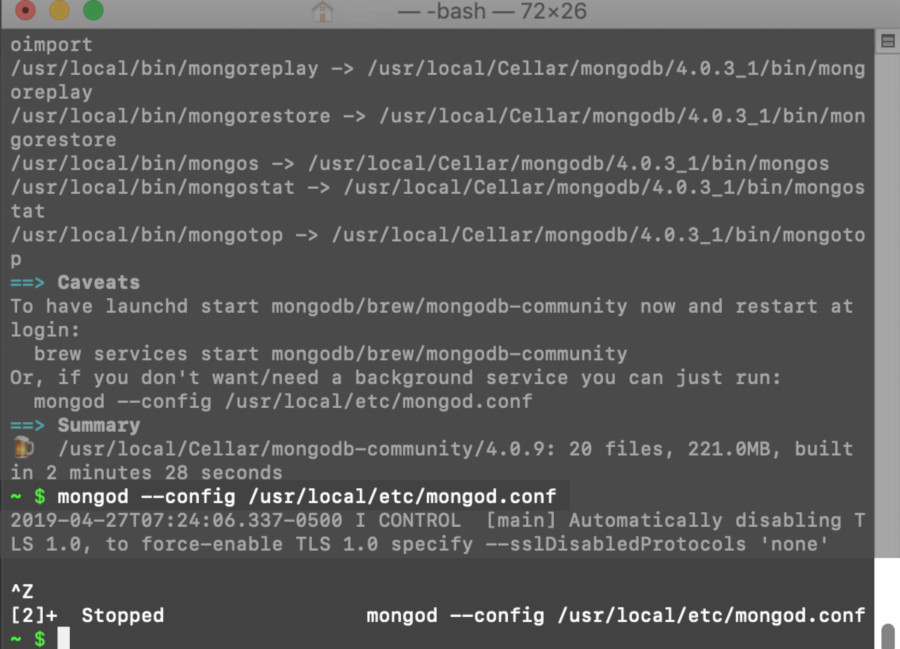
Use a TAR archive to Install MongoDB
We covered how to install MongoDB using Homebrew and that is the simplest way to do it. Now, we’ll show you how to install the MongoDB on macOS using a TAR archive. That’s right from the source.
First, download the most the latest stable release of the MongoDB for macOS. It’s the “macOS 64-bit x 64” option under “OS” on MongoDB’s Download Center.
Here, the current release version of MongoDB and the macOS 64-bit x64 options are selected on the MongoDB Download Center’s website.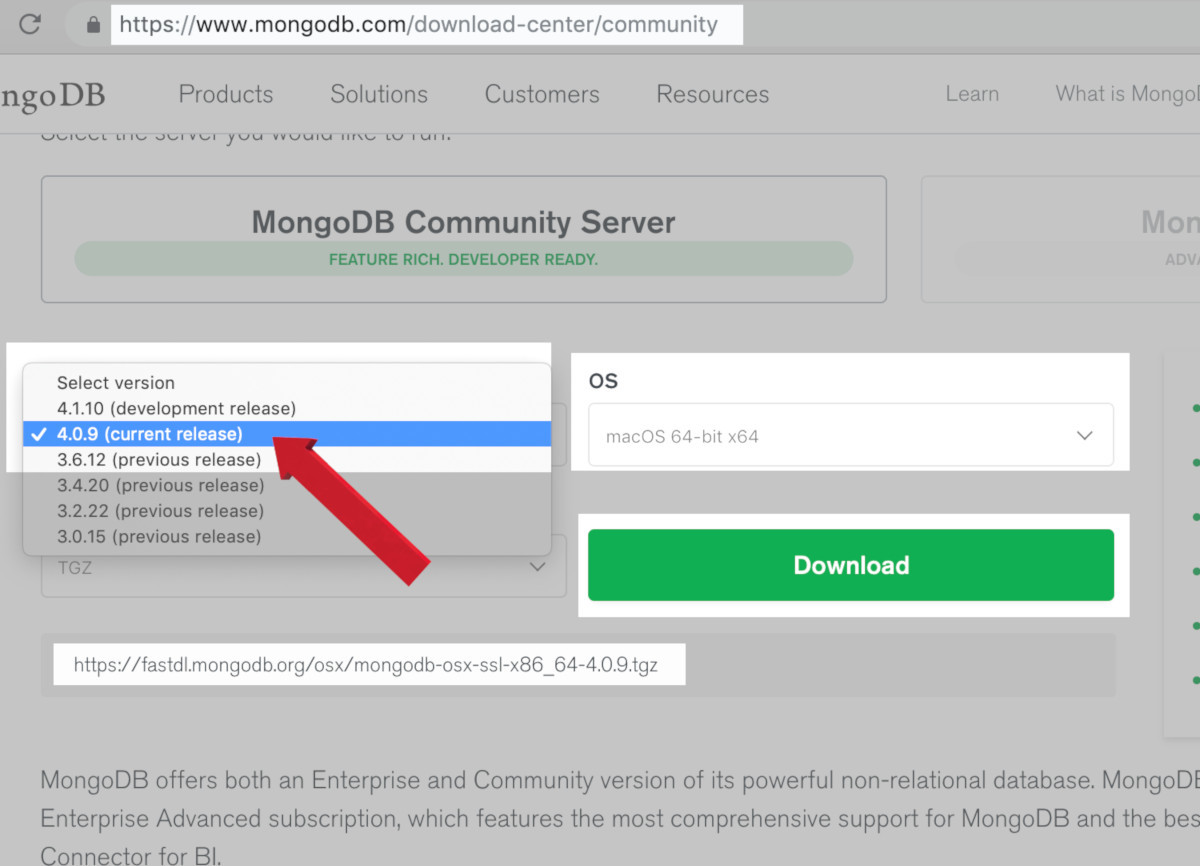
Open a macOS terminal window and switch to (
cd ~/Downloads)Downloadsdirectory.Use the command for
tgzarchives. Thetar xzfextracts the Tarball file. Make sure you have security privileges to make the changes usingsudocommands.A simple script installs MongoDB version 4.0.9 for macOS.
1 | sudo tar xzf mongodb-osx-ssl-x86_64-4.0.9.tgz |
- Verify that you have MongoDB database files. At a terminal prompt, type
/data/db. It’s not there if you get theNo such file or directoryresponse. If this happens, use the commandmkdirto make a new directory. Add the-p option. For the path you indicate, create the directory and associated sub-directories with thesudocommand.
1 | sudo mkdir -p /data/db |
Find out the username of the directory. The
whoamiis the command to use.The directory will need to have the necessary permissions and full ownership given to the user. Give them.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # get the user name: whoami # give ownership to the user: sudo chown {SOME_USER} /data/db # give permissions: sudo chmod -R 775 /data/ |
Configure the MONGO_PATH in the .bash_profile shell script
Find the hidden directory file
.bash_profilein the (cd ~) home directory. Usels -Ato find the hidden file.If the
.bash_profilescript isn’t there, create it withtouchcommand:
1 | sudo touch .bash_profile |
- If you find the
.bash_profile, edit it with a text editor. Usenanoif you like or use another text editor if you prefer:
1 | sudo nano .bash_profile |
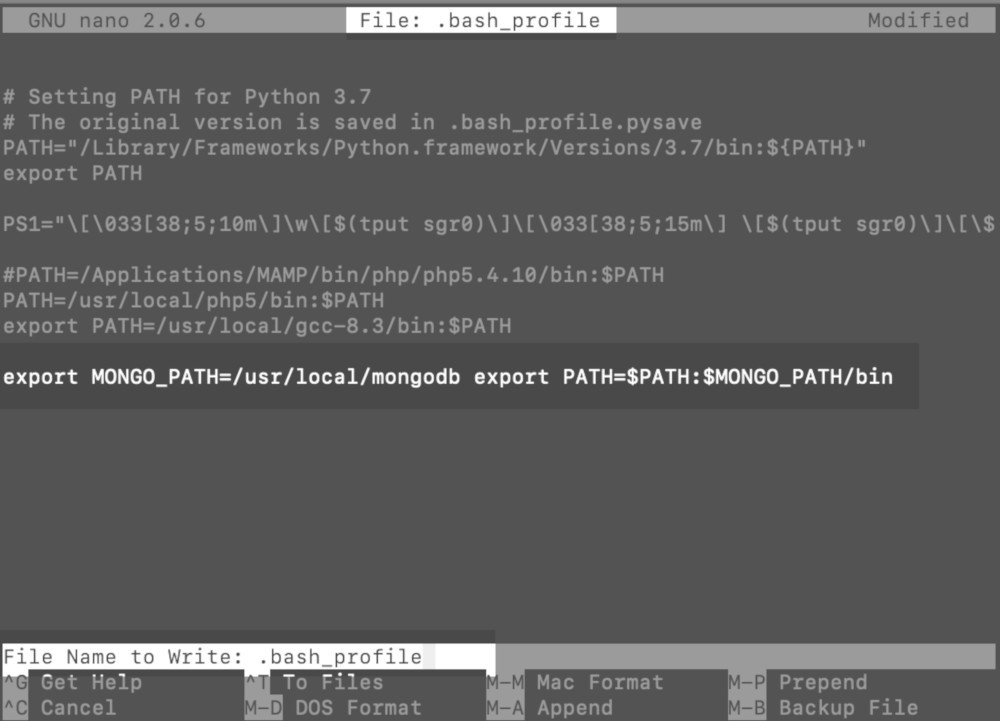
- Make sure to paste this code at the end of the script:
1 2 | export MONGO_PATH=/usr/local/mongodb export PATH=$PATH:$MONGO_PATH/bin |
The MongoDB working path is now set. Press CTRL+O to save the changes to the
bash_profileshell file, and then press CTRL+X to exit out ofnano.Make sure to restart the terminal or use the
source ~/.bash_profilecommand to reload the shell file’s settings and paths.Once the tarball archive is extracted make sure to move its contents to the
$PATHdirectory exported in the shell profile:
1 | sudo mv mongodb-osx-x86_64–4.x.x /usr/local/mongodb |
A screenshot of the .bash_profile shell script being edited with the nano text editor:
Start the MongoDB service on macOS
In the terminal window, start the service by typing
mongod.When you want to stop the MongoDB server, it’s the same as Homebrew. Press CTRL+C.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to install MongoDB server macOS. As you have learned, it’s easy to do. There are two common ways to install MongoDB: from the terminal using Homebrew or by way of the MongoDB website where you’ll use a Tarball archive. Together, macOS and MongoDB’s storage capabilities, indexing prowess, and analyzing ingenuity is all you need to propel your productivity day in and day out.
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started


