How to Insert MongoDB Documents Using Python
Introduction
Appending a MongoDB collection of documents is a basic part of document database management. Sometimes you’ll just need to insert one document; other times, you’ll need to insert many. The Python pymongo driver can help you efficiently accomplish either task.
Now is a great time to learn the way to insert MongoDB document Python because the insert_one() method and the pymongo driver were first introduced in PyMongo version 3. The older versions of PyMongo use the insertOne() method, which is less pythonic, so to speak. In other words, they’re obsolete.
Since the PyMongo version 3.x and the later ones contain the driver pymongo, you can harness its capabilities in all your coding tasks including adding documents to collections. Find out how to insert MongoDB documents using Python with this step-by-step tutorial today. If you’re already familiar with the insert document MongoDB Python process, and want to skip the details, feel free to go to Just the Code.
Prerequisites
MongoDB – Install MongoDB on the server.
Open a terminal window and check that it has been installed with the following command:
1 | mongo --version |
- Python 3 – Install the
pymongodriver, version Python 3.
>NOTE: Python 2 will soon be defunct.
- Here’s a tip for a fast install of Python 3: Use IDLE or any other Python environment you prefer. At the command line type
pip3 install pymongo. Check which driver version you have with it as well.
1 2 | import pymongo pymongo.version |
*Look for the version number in a string. For example, '3.4.0' is a hypothetical version number.
- If you see
ImportErrorin the results, reinstall Python becausepymongofailed to properly install.
Use the Python Class MongoClient to Connect MongoDB
- The class library needs to be imported at the script’s beginning for instantiation, the initialization of settings of new objects. Use the following command:
1 2 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 from pymongo import MongoClient |
- Now, you’re ready to create a MongoDB driver new instance:
1 | mongo_client = MongoClient() |
Pass the Parameters of the Port and Domain
- Here’s a URI string to explicitly pass both the port parameters and the domain right into MongoDB using
MongoClient().
1 | mongo_client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017') |
If you want to handle them each by themselves, pass the (Python) integer for the port and then for the domain name, use a string.
Alternatively, pass both as parameters, explicitly.
1 | mongo_client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017) |
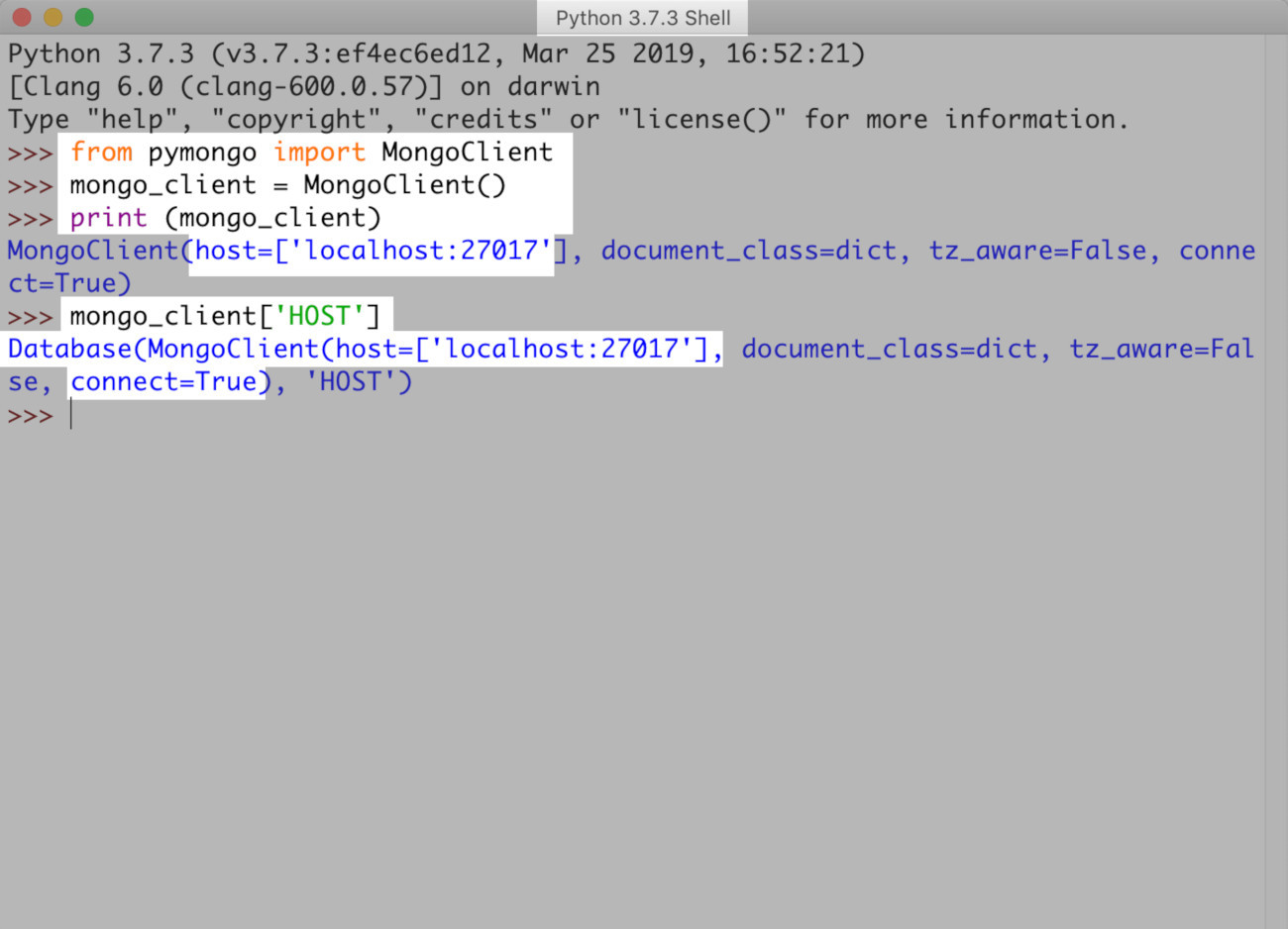
Verify your MongoDB server connection with a print statement in Python
- Here’s an environment of IDLE Python showing verification of an instance of the MongoDB client.
MongoDB is Ready for a Collection and Database
- Use
create_collection()to create a database as shown here:
1 2 3 4 | db = mongo_client.some_database # access "some_database" # create a new collection for the "some_database" database col = mongo_client.db.create_collection('collection_name') |
If you like, pass options such as the collection’s size and pipeline into the
create_collection().You can opt to declare a
collection_object. This allows you to create the document, collection, and database–all at once. The benefit of doing creating the document this way is that it may save you some time writing code. The MongoDB server won’t update until the document has been created.
1 | collection_object = db.some_collection |
- The above shows the declared collection object, but the MongoDB server has nothing written to it yet.
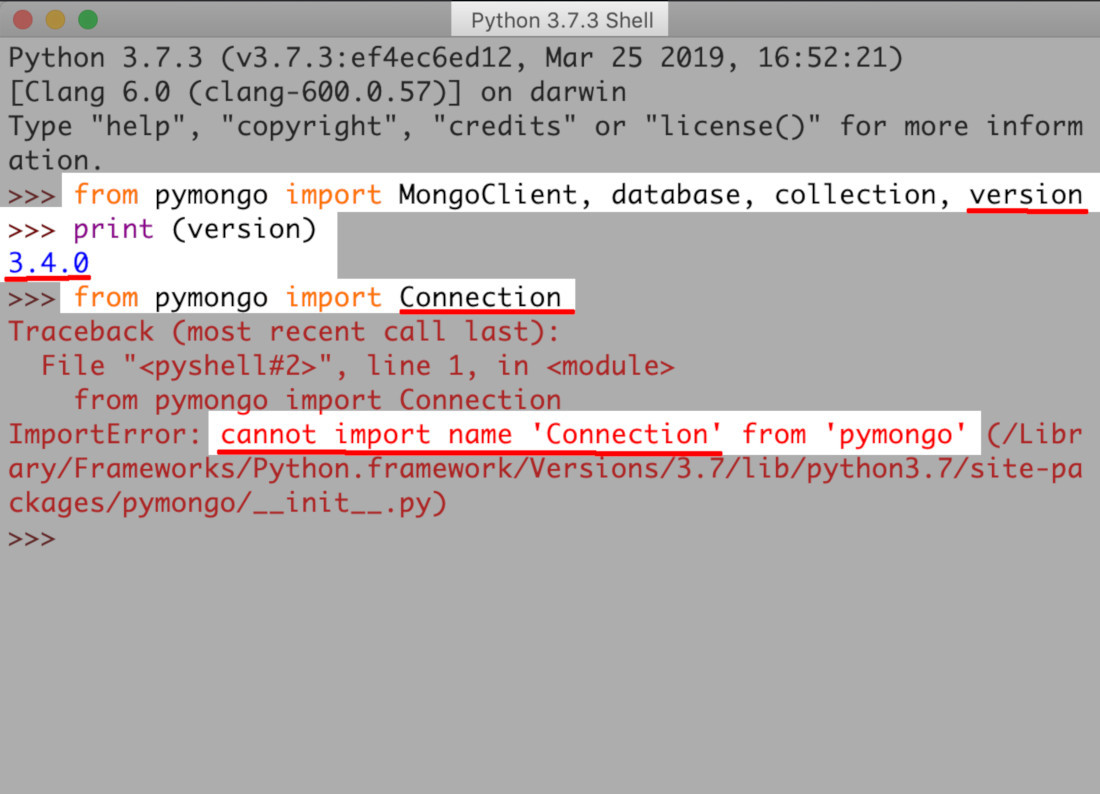
>NOTE: There are some limitations to the Connection class where it concerns the PyMongo 3 driver. Only in previous versions of PyMongo can the script accept the importation of the Connection class. This occurs because the Connection class for the library is outdated.
With the PyMongo 3 driver, an attempt to import the Connection class in Python IDLE returns an ImportError.
How to Insert Document MongoDB Python
MongoDB uses the JSON format and the
python_dictPython dictionary object matches it well.The example below shows KVP (key-value pairs) as unique identifiers for line values and their stated corresponding fields.
1 2 3 4 5 | python_dict = { "field1" : "value for field 1", "field2" : "value for field 2", "field3" : "value for field 3" } |
- Now, the
python_dictthat was just created can be put into the database as the document. Insert it using thepymongoinsertion method.
Create a New Document in MongoDB withinsert_one()
- After instantiation of the new collection and database, create document MongoDB Python and add the document with
insert_one().
1 | result_object = collection_object.insert_one(python_dict) |
Get Feedback from pymongo.results.InsertOneResult
- You can parse the object
pymongo.results.InsertOneResultto get useful API response feedback.
- Use the
result_object.acknowledgedandresult_object.inserted_id
1 2 | result_object.acknowledged # <-- should return: True result_object.inserted_id # <--- returns a bson ObjectId |
- Another way to do an API call is by the
ObjectIdof the document that was inserted. At the call’s end, call the attributeinserted_idlike this:
1 | result_id = collection_object.insert_one(another_doc).inserted_id |
>NOTE: About “ID” fields. You could think of them as unique index document MongoDB Python types of fields or index document MongoDB collection Python fields. The unique IDs such as ObjectID ensures that no two documents’ values are alike. By the way, Indexing speeds up finding relevant documents in your queries.
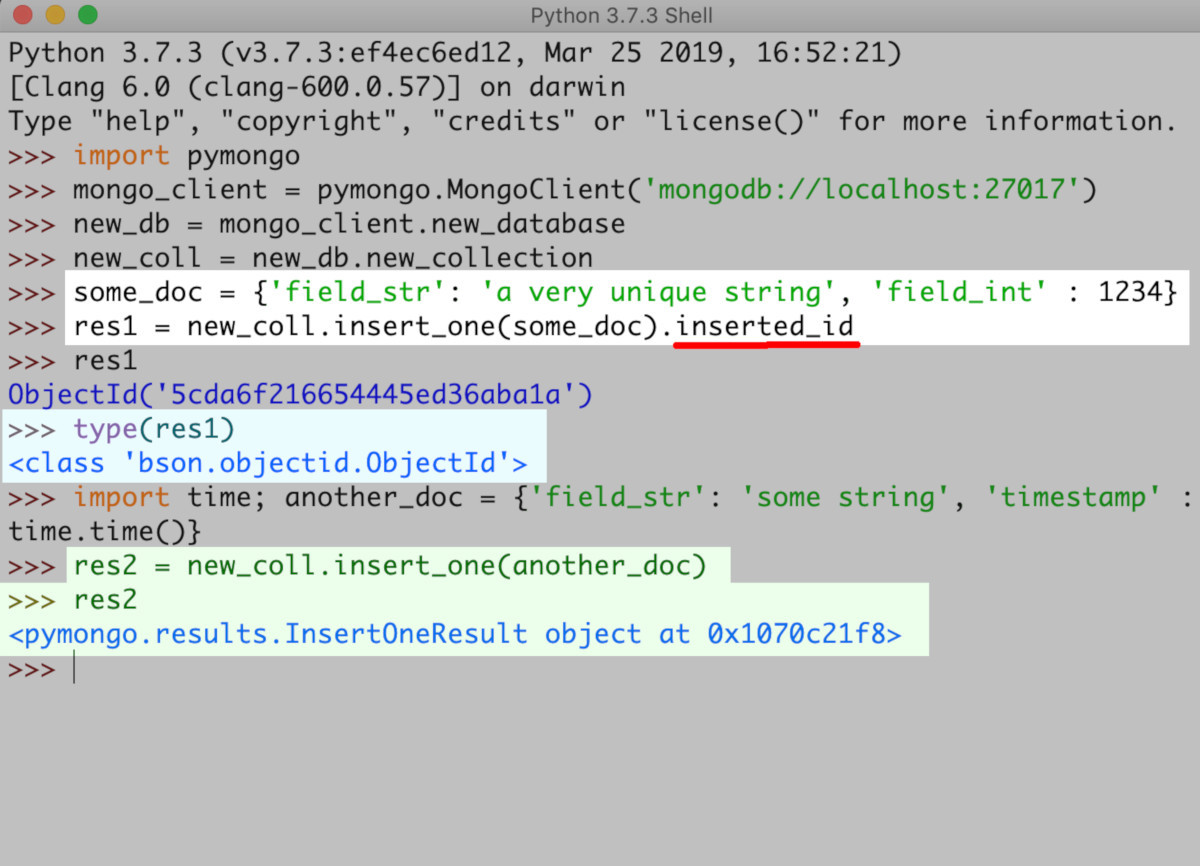
- The ObjectID BSON for the document has an alphanumeric ID that is unique. You’ll see it when the API call’s returned result is passed to the print function in Python.
1 | ObjectId('5cda6f216654445ed36aba1a') |
This example shows within the Python IDLE environment the inserted_id function. What’s more, the page indicates that for a collection, to add documents, PyMongo was used.
How to use the insert_many() method to insert multiple MongoDB documents
With the method,
insert_many(), you can insert Python dictionaries by the list as opposed to one at a time.To begin, start with an empty list and delcare it with this command:
1 | my_documents = [] |
Add documents to a Python list
When you want to create a document MongoDB Python, that is to create a MongoDB document, create a Python dictionary for it.
Use
my_documentsCreate a Python dictionary for each MongoDB document you’d like to create.
1 2 3 4 | # Add the MongoDB documents to a Python list my_documents += [{'field': 'value'}] my_documents.append({'field': 'value'}) my_documents = my_documents + [{'field': 'value'}] |
Use the method insert_many() to pass the MongoDB documents list
- A result object will be returned when you pass the list of MongoDB documents via the
insert_many()method.
1 2 | result = collection_object.insert_many(my_documents) print (result) |
- Here is a successful returned result object looks like:
1 | <pymongo.results.insertmanyresult object="object" at="at" 0x10cd257e0="0x10cd257e0"> |
Iterate a collection of documents in MongoDB with the for loop
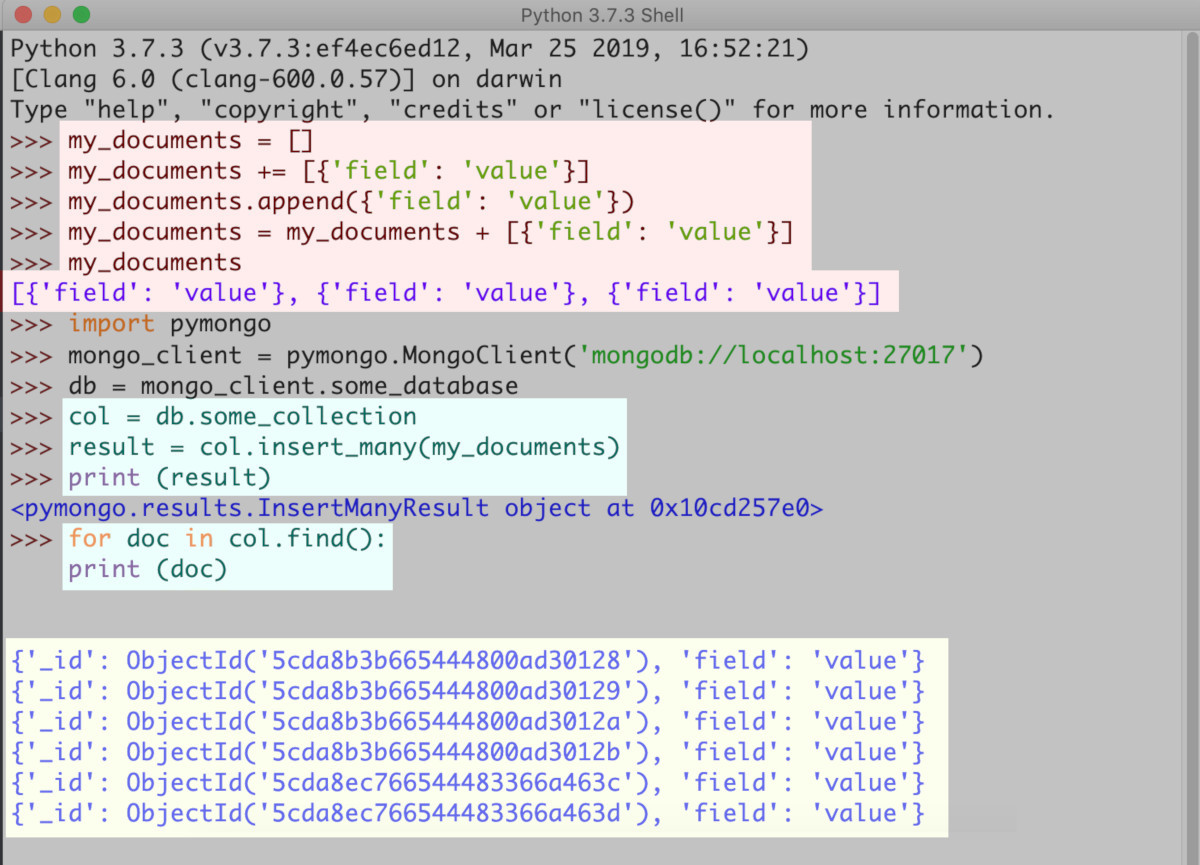
- Below is an example of the Python IDLE environment using the
forloop method andinsert_manyto add documents to a collection in MongoDB.
>TIP: Now you can index document MongoDB collection Python for your updated collection to streamline finding your documents. You can also index document MongoDB Python if you just added them separately. Indexing improves scanning your queries.
Conclusion
Insert MongoDB document Python is more simplified when you use the insert_one() method to insert one document. You can also streamline the process of inserting more than one document at a time when you do it with insert_many() method. What makes it all happen expeditiously is pymongo, Python’s driver which was first available in Python version 3.x. Now it’s a standard feature in later editions of Python. Take advantage of the insert methods discussed in this tutorial. Try them on your next coding project and you’ll likely save time while increasing productivity.
Just the Code
Here’ the complete script showing how to use Python to insert one or more MongoDB documents into a collection.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 #-*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import the pymongo library from pymongo import time # create a client instance with explicitly passed host parameter mongo_client = pymongo.MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017') # create a new MongoDB database object for the client db = mongo_client.new_database # create a collection object that will be # used to call 'insert' methods col = db["Collection With Spaces"] # create the Python dictionaries to be passed as Mongo documents some_doc = {'field_str': 'a very unique string', 'field_int' : 1234} # create another document with a timestamp another_doc = {'field_str': 'some string', 'timestamp' : time.time()} # call the 'insert_one()' method to insert a doc result = col.insert_one(some_doc).inserted_id print ("nresult of insertion:", result) # insert another document result = col.insert_one(another_doc).inserted_id print ("result of insertion:", result) # create a list and append several documents # (in the form of Python dictionaries) to it my_documents = [] # three different ways to append items to a Python list my_documents += [{'field': 'value'}] my_documents.append({'field': 'value'}) my_documents = my_documents + [{'field': 'value'}] # call the `insert_many()` method and return a result result = col.insert_many(my_documents) print ('ninsert_many result:',result) |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started




