How to Insert MongoDB Documents from JSON using the Golang Driver
Introduction
This tutorial will explain how to insert MongoDB documents from JSON using the Golang driver. When using the Golang driver to insert MongoDB documents from a JSON file with Golang, MongoDB automatically creates a collection at the time of insertion, so no preexisting documents or collections are required. However, there must be a few MongoDB documents stored in a JSON file on the MongoDB server.
Prerequisites for Indexing MongoDB Documents in a JSON using Golang
MongoDB must be installed and running on the server making the Golang API calls. Execute the
mongodcommand in a terminal window to obtain information about the MongoDB daemon processes.Golang must be installed on the same machine and the MongoDB project directory must be in Go’s
$GOPATH. More information may be obtained by typinggo help gopathor$GOPATHin a terminal window.Confirm the
mongo-go-driverpackage library is installed in the project’s directory in the$GOPATHof the server. Execute the followinggo getcommand to install the driver:
1 | go get go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo |
How to Create a JSON File for the MongoDB Documents
As MongoDB automatically creates a database and collection at the time of insertion, there does not have to be any preexisting documents or collections on the MongoDB server. However, there must be a few MongoDB documents stored in a .json file.
The MongoDB JSON documents must be placed inside a JSON array within square brackets [] and each document must be delimited with a comma (,).
Following are a few JSON example used in this tutorial to insert MongoDB documents:
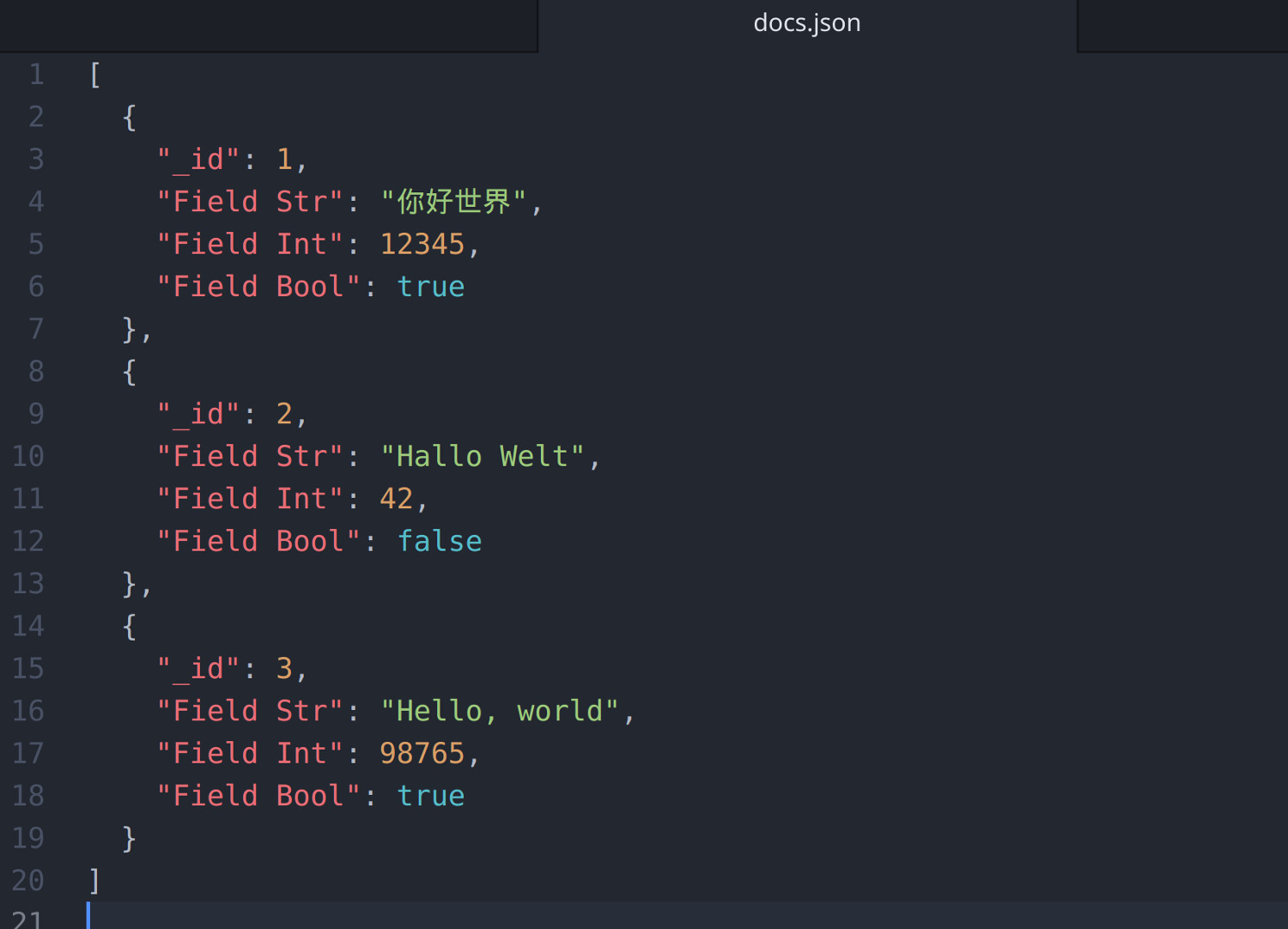
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | [ { "_id": 1, "Field Str": "ä½ å¥½ä¸–ç•Œ", "Field Int": 12345, "Field Bool": true }, { "_id": 2, "Field Str": "Hallo Welt", "Field Int": 42, "Field Bool": false }, { "_id": 3, "Field Str": "Hello, world", "Field Int": 98765, "Field Bool": true } ] |
NOTE: As shown in the below script and image, if the JSON file must be loaded from a relative path outside the $GOPATH, then the path/filepath package can be used to load the file:
1 2 | docsPath, _ := filepath.Abs("/path/to/json/file/docs.json") byteValues, err := ioutil.ReadFile(docsPath) |
How to Import the MongoDB and Go Packages in a Golang Script
First, declare the main() function with the package keyword and then import all of the Golang packages, including the mongo-driver package libraries, as shown in the following script:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "io/ioutil" // io.ReadFile "log" "reflect" // get an object type "time" // Import the JSON encoding package "encoding/json" // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) |
How to Declare a Go Struct for the MongoDB JSON Document Fields
Execute the following script to create a new struct datatype for the MongoDB fields that can be used to map the JSON data to the respective MongoDB fields:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | type MongoFields struct { //Key string `json:"key,omitempty"` ID int `json:"_id"` FieldStr string `json:"Field Str"` FieldInt int `json:"Field Int"` FieldBool bool `json:"Field Bool"` } |
The JSON struct tags strings must be defined so the tags are perfectly matched to the actual MongoDB fields in the JSON documents. For example, the JSON document must be json:"some_field" if the MongoDB field is “some_field”, regardless of how the struct’s variable is named.
How to Declare the Main() Function and Connect to MongoDB using the Golang Driver
Execute the following command to declare the main() function and connect to MongoDB using the client library:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | func main() { // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "n") // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("mongo.Connect() ERROR: %v", err) } |
How to Create a Golang Context Object for the MongoDB API Calls
The following is an example of how to create a Context object with a timeout of three seconds.
1 2 | // Declare Context type object for managing multiple API requests ctx, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second) |
The "time" package must be imported or a basic context object with context.Background() must be instantiated.
Now pass the ctx object instance to the MongoDB API calls.
How to Instantiate a Collection Object from the MongoDB Client Instance
If the collection or database name doesn’t exist, then MongoDB will create it when the JSON documents are inserted with the following script:
1 2 3 | // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("JSON_docs").Collection("JSON Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "n") |
How to Import the JSON File with the Golang’s ‘ioutil’ Package
Go programming language has a package called ioutil that allows for the importation of data into the Golang script from a file.
Read the JSON file using ioutil.ReadFile()
Execute the following script to read the JSON file and return a int8[] byte slice using the ioutil.ReadFile() method to check for any errors:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | // Load values from JSON file to model byteValues, err := ioutil.ReadFile("docs.json") if err != nil { // Print any IO errors with the .json file fmt.Println("ioutil.ReadFile ERROR:", err) } else { // Print the values of the JSON docs, and insert them if no error fmt.Println("ioutil.ReadFile byteValues TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(byteValues)) fmt.Println("byteValues:", byteValues, "n") fmt.Println("byteValues:", string(byteValues)) |
If no errors are returned, proceed to unmarshal the JSON documents from the byte slice.
How to Unmarshal the Byte Slice and Create MongoDB Struct Documents
Execute the following commands to declare an empty Go slice for the MongoFields struct objects and make an empty slice array for the “MongoFields” struct objects to be stored:
1 2 | // Declare an empty slice for the MongoFields docs var docs []MongoFields |
How to Pass the Bytes Slices to the Unmarshal() Method
Execute the following command to pass the bytes slices to the JSON library’s Unmarshal() method and put slices into the docs struct slice using a pointer (&):
1 2 3 4 5 | // Unmarshal the encoded JSON byte string into the slice err = json.Unmarshal(byteValues, &docs) // Print MongoDB docs object type fmt.Println("nMongoFields Docs:", reflect.TypeOf(docs)) |
How to Iterate the MongoDB Documents and Call the Golang Driver’s InsertOne() Method
The final step is to iterate over and parse the MongoDB struct documents so the data can be passed to the MongoDB client library’s InsertOne() method.
Execute the following command to use “range” to iterate the slice of the MongoDB documents:
1 2 | // Iterate the slice of MongoDB struct docs for i := range docs { |
How to pass each document iteration to the InsertOne() method
Use the following script to pass the struct document to the Collection object’s InsertOne() method and check for errors:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | // Put the document element in a new variable doc := docs[i] fmt.Println("ndoc _id:", doc.ID) fmt.Println("doc Field Str:", doc.ID) // Call the InsertOne() method and pass the context and doc objects result, insertErr := col.InsertOne(ctx, doc) |
Check for any API MongoDB insertion errors
Execute the following script to print the result of the MongoDB API call:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | // Check for any insertion errors if insertErr != nil { fmt.Println("InsertOne ERROR:", insertErr) } else { fmt.Println("InsertOne() API result:", result) } } } } |
Conclusion
This tutorial demonstrated how to use the Golang driver to insert MongoDB documents from JSON with Golang and insert multiple documents, stored in a JSON file, into a MongoDB collection as shown in the following image:
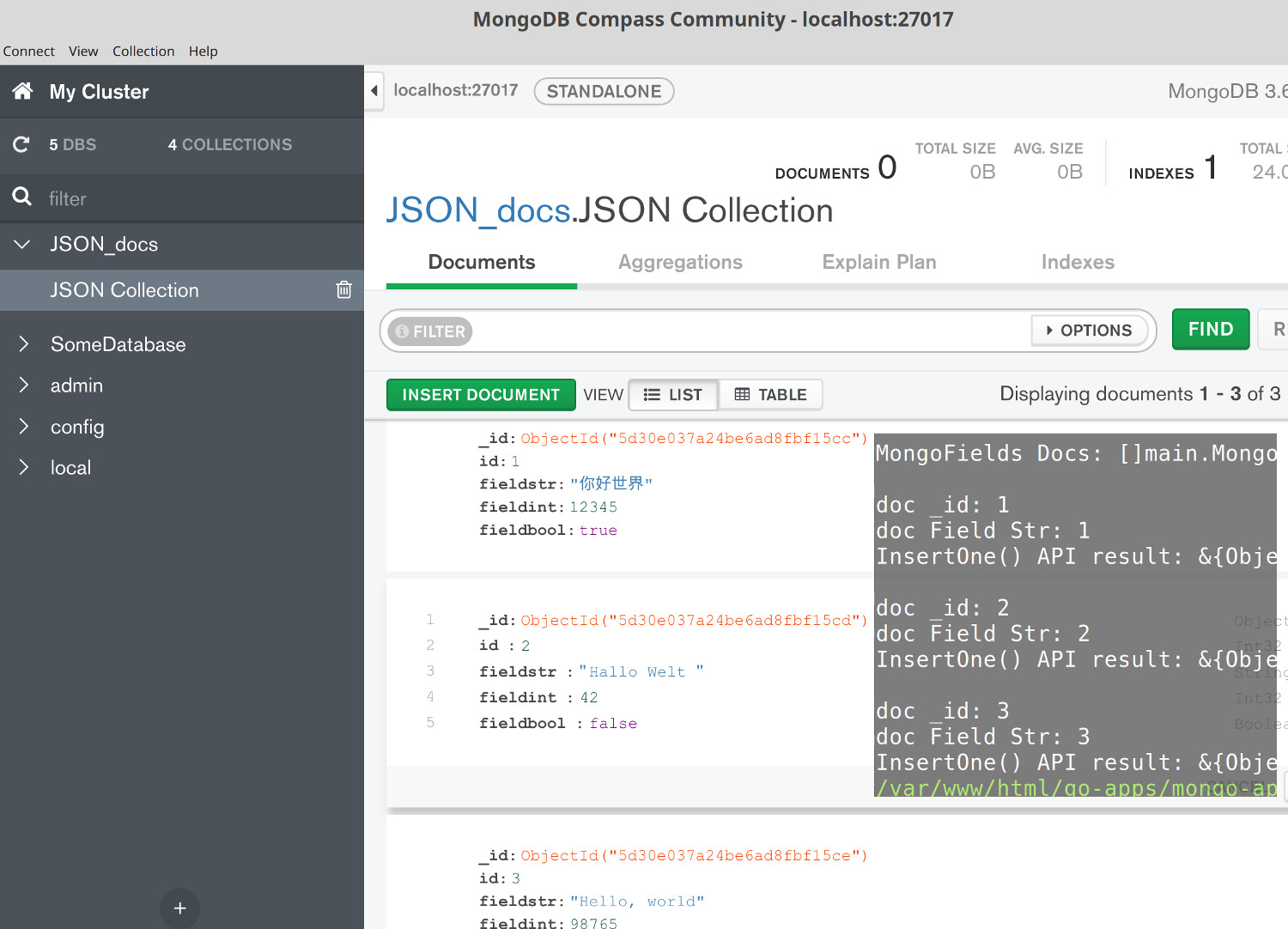
The article covered how to import the MongoDB and Go packages in a Golang script and to iterate the MongoDB documents. The tutorial also covered how to call the Golang driver’s InsertOne() method, how to instantiate a collection object from the MongoDB Client instance and how to check for any API MongoDB insertion errors. Remember that when creating a Golang Context object for the MongoDB API calls either the "time" package must be imported or a basic context object with context.Background() must be instantiated.
Just the Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "io/ioutil" // io.ReadFile "log" "reflect" // get an object type "time" // Import the JSON encoding package "encoding/json" // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) type MongoFields struct { //Key string `json:"key,omitempty"` ID int `json:"_id"` FieldStr string `json:"Field Str"` FieldInt int `json:"Field Int"` FieldBool bool `json:"Field Bool"` } func main() { // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "n") // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("mongo.Connect() ERROR: %v", err) } // Declare Context type object for managing multiple API requests ctx, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 3*time.Second) // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("JSON_docs").Collection("JSON Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "n") // Load values from JSON file to model byteValues, err := ioutil.ReadFile("docs.json") if err != nil { // Print any IO errors with the .json file fmt.Println("ioutil.ReadFile ERROR:", err) } else { // Print the values of the JSON docs, and insert them if no error fmt.Println("ioutil.ReadFile byteValues TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(byteValues)) fmt.Println("byteValues:", byteValues, "n") fmt.Println("byteValues:", string(byteValues)) // Declare an empty slice for the MongoFields docs var docs []MongoFields // Unmarshal the encoded JSON byte string into the slice err = json.Unmarshal(byteValues, &docs) // Print MongoDB docs object type fmt.Println("nMongoFields Docs:", reflect.TypeOf(docs)) // Iterate the slice of MongoDB struct docs for i := range docs { // Put the document element in a new variable doc := docs[i] fmt.Println("ndoc _id:", doc.ID) fmt.Println("doc Field Str:", doc.ID) // Call the InsertOne() method and pass the context and doc objects result, insertErr := col.InsertOne(ctx, doc) // Check for any insertion errors if insertErr != nil { fmt.Println("InsertOne ERROR:", insertErr) } else { fmt.Println("InsertOne() API result:", result) } } } } |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started



