How To Import and Export MongoDB Data Using Pandas In Python
Introduction
With the Python Pandas library, you can effortlessly import and export documents. This includes insert documents MongoDB Python, import data MongoDB Pandas, doing a bulk insert PyMongo, and conducting an export data MongoDB Pandas. You can also import data MongoDB Python and insert data MongoDB Pandas.
All of these essential tasks allow you to organize, iterate, and analyze large amounts of MongoDB data on a regular basis in your API method calls. Use both the NumPy library and the Pandas library to export data MongoDB Python and to insert MongoDB document Python because they give you the advantage to get things done with ease.
This step-by-step tutorial shows you how to import and export MongoDB data using Pandas in Python. If you are familiar with how Pandas and NumPy libraries work to export and insert document MongoDB Pandas and want to skip reading this in-depth tutorial, go to Just the Code.
Prerequisites
- Python 3 – Download it and confirm it is running. You can use the PIP package manager to install it.
>NOTE: Python 2 is about to be obsolete. This tutorial shows many examples based on Python 3, but there are a few references to Python 2, and those are identified.
- MongoDB – Install it and verify it is running. The command called process status (
ps) tells you how many occurrences of MongoDB are running:
1 | ps -ax | grep mongo |
- To practice API method call testing of these examples, create a test database that has collection of data.
MongoDB PyMongo Python driver
- Use
pip3to install the PyMongo library to gain MongoDB server access.
1 | pip3 install pymongo |
The NumPy library and Pandas library
It’s best to use
pip3and install both NumPy and Pandas libraries to gain access to all methods and attributes.Install the NumPy library first.
1 | pip3 install numpy |
- After NumPy has finished with the installation, proceed to install the Pandas library.
1 | pip3 install pandas |
Make a Python script and import the libraries
At the top of the Python script, import the libraries for Numpy, Pandas, and the MongoDB client.
Use the alias np to import NumPy
- The NumPy library can be imported with
import numpy. To make the process faster, just use the aliasnp.
1 | import numpy as np |
Use the alias pd to import Pandas
- The Pandas library can be imported with
pandas. To make the process faster, if you want, you can use the aliaspd.
>NOTE: The example below uses pandas instead of its alias, pd, for readability.
1 | import pandas |
Make a PyMongo class instance
- Import the
MongoClientclass from PyMongo. After that, you’ll be able to make MongoDB API calls.
1 | from pymongo import MongoClient |
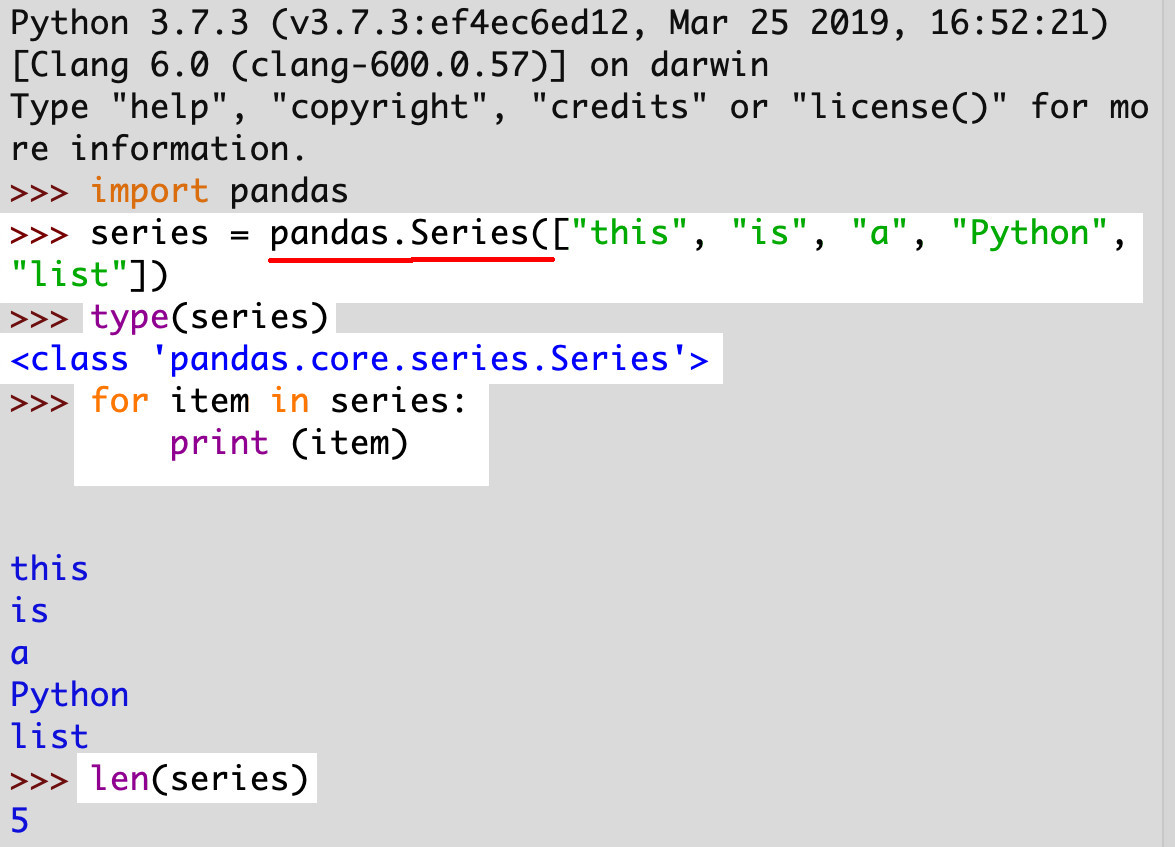
Create a simple pandas.Series with the Series() method
- Use the
Series()class method of the Pandas Library and pass a Python list to it in order to have an object returned. That’s how you construct aSeries()object.
>NOTE: A basic Pandas Series object is a NumPy array that is one-dimensional. It uses an index which is organized with labels.
1 | series = pandas.Series(["this", "is", "a", "Python", "list"]) |
Use enumerate() to iterate Pandas Series object
- Just like a list, the
enumerate()function iterates thepandas.core.series.Seriesobject.
1 2 | for num, item in enumerate(series): print (num, '--', item) |
Use the Series’ index method to pass one more Python list
- Make sure the additional Python list has the same elements that which you want an index created.
1 | series.index = ["Row 1", "Row 2", "Row 3"] |
Bypass the exception ValueError: <span>Length mismatch
- Compare lists for the length of
Serieswith the new index to dodge the exceptionValueError: Length mismatch. The element number should be the same for both lists.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | series = pandas.Series(["TOO", "MANY", "ELEMENTS", "FOR", "INDEX"]) my_index = ["Row 1", "Row 2", "Row 3"] if len(series) == len(my_index): series.index = my_index elif len(series) < len(my_index): print ("The index list is too long!") elif len(series) > len(my_index): print ("The index list is too short!") |
Verify the index of the Series object
- The
valuesindex’s attribute is what you can all to confirm the Series object’s index.
1 | print (series.index.values) |
- Integers cover the object list’s length and it starts with
0and continues on from there. (For example,array ([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7]).)
Create a Panda DataFrame object
A
ValueErrorerror will be returned if yourDataFrameis missing one or more of the following:SeriesPanda objectsDataFramePanda objectsndarrayNumPy objects- Python dictionaries, or dictionaries that are one-dimensional lists,
ndarrays,Series, NumPy arrays
>NOTE: The DataFrame class in Panda is a two-dimensional type of Series array. It returns a scalable list object.
- The example below is a basic build array for a
DataFrameobject.
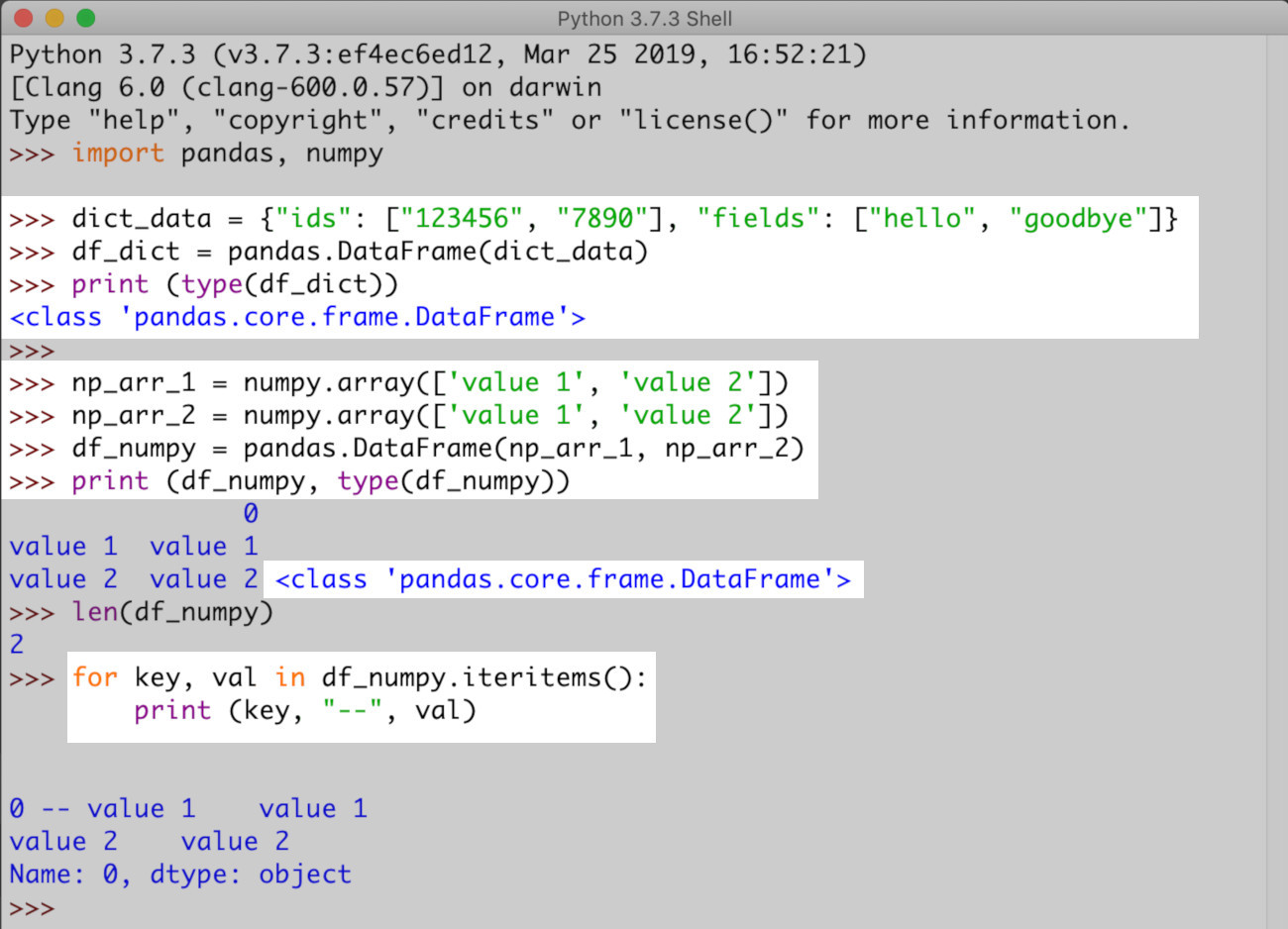
1 2 3 | # create a DF object from a nested dictionary object dict_data = {"ids": ["123456", "7890"], "fields": ["hello", "goodbye"]} df_dict = pandas.DataFrame(dict_data) |
- Now for an example of
NumPyobjects from which aDataFrameis created.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | # create a few ndarray NumPy arrays np_arr_1 = np.array(['value 1', 'value 2']) np_arr_2 = np.array(['value 1', 'value 2']) # put the NumPy arrays together and form a Pandas DataFrame object df_numpy = pandas.DataFrame(np_arr_1, np_arr_2) print (df_numpy, type(df_numpy)) |
Iterate fast with the method intertuples()
- Although you can iterate fine with
iteritems()oritems(), useitertuples()to iterate theDataFrameobject in Pandas much more quickly.
1 2 3 | # use the itertuples() method to iterate a DataFrame object for row in df.itertuples(): print (row) |
Do a MongoDB document DataFrame and Pandas’ Series conversion
- Converting MongoDB documents with
DataFrameandSerieshas benefits. You can either convert MongoDB documents by defining the data types of the fields, and if you have just one data type field in a MongoDB collection, it’s even easier to specify.
How to Construct MongoDB collection document field Pandas Series objects
- With Pandas, there’s a good way to analyze a complete MongoDB collection’s data based on an API call. You can use the
find()method.
Make an API call using find() to import document data
First, create a
MongoClientinstance to import the library.Next, build a database and Pandas collection.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # build a new client instance for MongoClient mongo_client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017) # create new database and client collection db = mongo_client.pandas_database col = db.pandas_collection |
- Time to use the
find()method, the API call to locate the MongoDB documents within the collection.
1 2 | # API call to MongoDB collection mongo_docs = col.find() |
Make NumPy arrays Python dictionary
Construct a dictionary object that is empty. Next, obtain MongoDB documents data with iteration. Then make NumPy object arrays
ndarrayfrom the data.A new dictionary key will be created unless one already exists. See the example below for the script.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | # create an empty dictionary for the MongoDB documents' fields fields = {} # go through list of MongoDB documents for doc in mongo_docs: # iterate key-value pairs of each MongoDB document # use iteritems() for Python 2 for key, val in doc.items(): # attempt to add field's value to dict try: # append the MongoDB field value to the NumPy object fields[key] = np.append(fields[key], val) except KeyError: # create a new dict key will new NP array fields[key] = np.array([val]) # print out the fields dictionary print (fields) |
- Use iteration to make
pymongo.cursor.Cursorobjects out of the returned data.
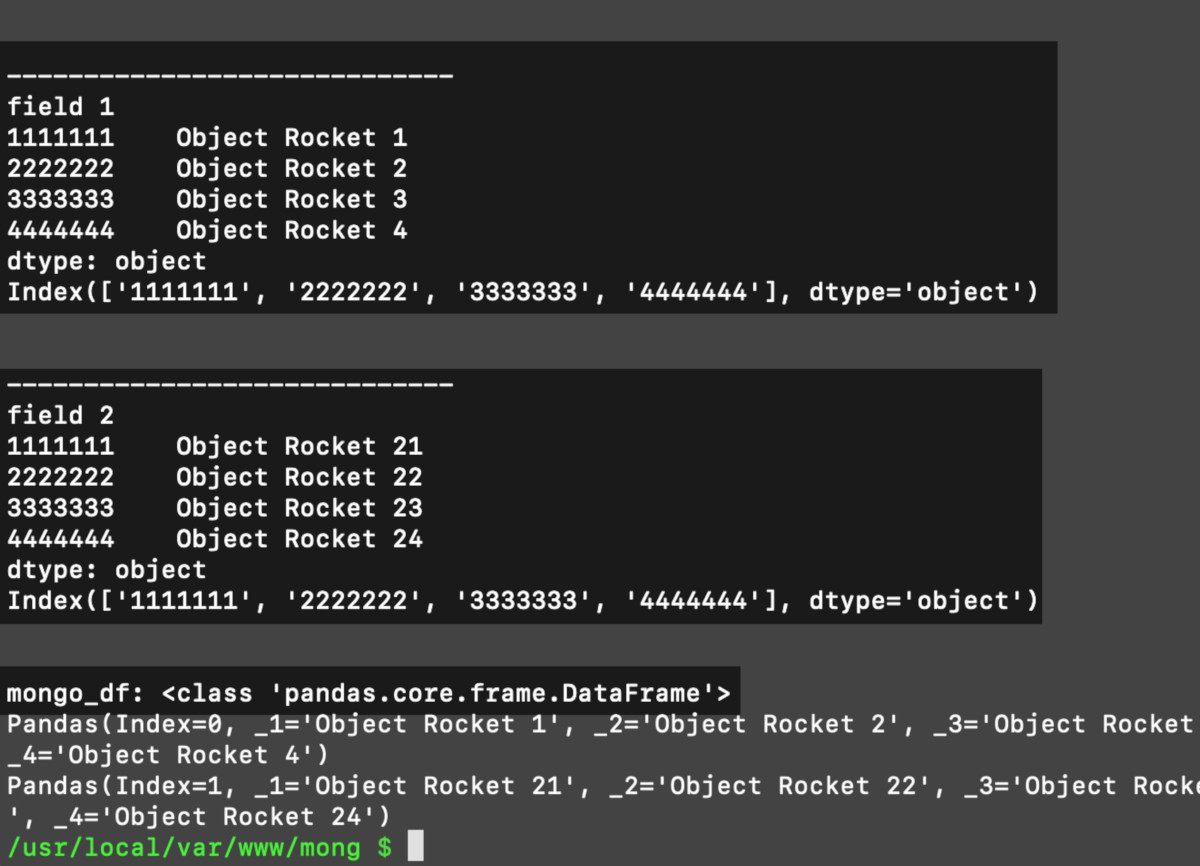
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | # create an empty list for the Series objects series_list = [] # iterate over the dict of lists for key, val in fields.items(): # convert the 'fields' NumPy arrays into Pandas Series if key != "_id": fields[key] = pandas.Series(fields[key]) fields[key].index = fields["_id"] print ("\n\n-----------------------------") print (key) print (fields[key]) print (fields[key].index) # put the series with index into a list series_list += [fields[key]] |
Use the Pandas Series arrays list and construct a DataFrame object
Make a
DataFramedictionary object from the data in the PandasSeries.The
DataFrame()class is where you pass the dictionary.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | # create a dictionary for the DataFrame frame dict df_series = {} for num, series in enumerate(series_list): # same as: df_series["data 1"] = series df_series['data ' + str(num)] = series # create a DataFrame object from Series dictionary mongo_df = pandas.DataFrame(df_series) print ("\nmongo_df:", type(mongo_df)) |
The MongoDB document data’s DataFrame iteration is now ready to print
You did it! Iterate the Series objects inside the DataFrame and the DataFrame itself.
1 2 3 4 5 6 | # iterate over DataFrame object for series in mongo_df.itertuples(): for num, item in enumerate(series): print (item) print (series) print ("\n") |
>NOTE: You can easily create meaningful graphs and chart data for detailed analyzation when you group the MongoDB field data in aggregate.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed you how to process MongoDB document data using Pandas and NumPy. Both libraries help you to simplify handling import data MongoDB Python, insert document MongoDB Pandas, export data MongoDB Pandas, and insert MongoDB document Python. You can also bulk insert PyMongo, insert documents MongoDB Python, and insert data MongoDB Pandas.
Within the lesson, you discovered how to create a simple pandas.Series object, use the enumerate() function, and avoid a ValueError: Length mismatch exception. This tutorial covered much more to help you iterate, organize, and import data MongoDB Pandas and export data MongoDB Python to evaluate a MongoDB collection.
Read Just the Code below and use it as a handy aid for your current and future projects.
Just the Code
Use the example script below as a quick reference guide for this tutorial on how to import and export MongoDB using Pandas in Python.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 #-*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import the MongoClient class from pymongo import MongoClient # import the Pandas library import pandas # import the NumPy library as an alias import numpy as np # build a new client instance of MongoClient mongo_client = MongoClient('localhost', 27017) # create new database and collection instance db = mongo_client.pandas_database col = db.pandas_collection ''' # API call to MongoDB collection mongo_docs = col.find() for doc in mongo_docs: _id = doc["_id"] print (doc) print (mongo_docs) ''' """ Use this dictionary to simulate a call to a MongoDB server, or use find() to pull your own data with an API call to MongoDB """ mongo_docs = [ {"_id": "1111111", "field 1" : 'Object Rocket 1', "field 2" : 'Object Rocket 21'}, {"_id": "2222222", "field 1" : 'Object Rocket 2', "field 2" : 'Object Rocket 22'}, {"_id": "3333333", "field 1" : 'Object Rocket 3', "field 2" : 'Object Rocket 23'}, {"_id": "4444444", "field 1" : 'Object Rocket 4', "field 2" : 'Object Rocket 24'} ] # create an empty dictionary for the MongoDB documents' fields fields = {} # go through list of MongoDB documents for doc in mongo_docs: # iterate key-value pairs of each MongoDB document # use iteritems() for Python 2 for key, val in doc.items(): # attempt to add field's value to dict try: # append the MongoDB field value to the NumPy object fields[key] = np.append(fields[key], val) except KeyError: # create a new dict key will new NP array fields[key] = np.array([val]) # print out the fields dictionary print (fields) # create an empty list for the Series objects series_list = [] # iterate over the dict of lists for key, val in fields.items(): # convert the 'fields' NumPy arrays into Pandas Series if key != "_id": fields[key] = pandas.Series(fields[key]) fields[key].index = fields["_id"] print ("\n\n-----------------------------") print (key) print (fields[key]) print (fields[key].index) # put the series with index into a list series_list += [fields[key]] # create a dictionary for the DataFrame frame dict df_series = {} for num, series in enumerate(series_list): # same as: df_series["data 1"] = series df_series['data ' + str(num)] = series # create a DataFrame object from Series dictionary mongo_df = pandas.DataFrame(df_series) print ("\nmongo_df:", type(mongo_df)) # iterate over DataFrame object for series in mongo_df.itertuples(): for num, item in enumerate(series): print (item) print (series) print ("\n") |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started




