How To Insert A MongoDB Document Using The Golang Driver
Introduction
This tutorial will cover how to insert a MongoDB document with Golang into a collection. The tutorial explains the InsertOne() method of the official Golang driver (mongo-go-driver) for MongoDB, how to create a MongoDB document with Golang and how to import the needed MongoDB and Golang packages. MongoDB, Golang the official Golang driver for MongoDB must be installed to insertone MongoDB with Golang.
Prerequisites for Creating a MongoDB Index in Golang
MongoDB must be running. Enter
mongoto confirm the Mongo shell is properly installed and functioning.Golang must also be installed and running on the same machine as MongoDB with the
$GOPATHdirectory set for the Golang project.The official Golang driver for MongoDB must be installed on the machine’s
$GOPATHas shown here:
1 | go get go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo |
NOTE: If the database and collection do not already exist, both will be created on-the-fly, along with the document, by MongoDB once the insertion API call is made.
How to Connect to MongoDB Using a Golang Script
The API call must be done in a Golang script using the .go file extension. Create one in a folder, finder window or by executing the touch command in the terminal. Note that package main must be included at the top of the script.
How to import the needed MongoDB and Golang packages
Use the following Golang’s import statement to import the Golang and MongoDB packages to create an index:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "os" // os.Exit(1) on Error "reflect" // get an object type "time" // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) |
How to Declare a Golang Struct for the MongoDB Fields
The Golang driver uses the struct object to setup the MongoDB fields for data insertion and other API calls. As shown below, declare a new struct including all of the necessary fields for the MongoDB document being inserted:
1 2 3 4 5 | type MongoFields struct { FieldStr string `json:"Field Str"` FieldInt int `json:"Field Int"` FieldBool bool `json:"Field Bool"` } |
Notice the datatype of each new field needs to be explicitly passed and then followed by a json:"Name of Field" string that indicates the JSON content-type of the field. The above example calls the data structure MongoFields, but data structure can be given any name.
How to Connect to MongoDB Using the Golang Driver’s options.Client() Method
Use the below func keyword to declare the main() function where the data insertion and MongoDB insertOne() API call will take place:
1 | func main() { |
How to connect to MongoDB in Golang
Declare a new options.Client() instance inside the main() function that will be used to create a new connection to MongoDB. Change the host and port URI settings, as shown below, to match the server’s domain and MongoDB settings:
1 2 3 | // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions type:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "\n") |
Execute the following command to pass the clientOptions instance to the mongo.Connect() method and make sure to pass a context.TODO() object with it:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { fmt.Println("mongo.Connect() ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } |
How to Create a Context Object for the MongoDB API Calls
Use the time package, as shown below, to create a new context instance that can be used to manage multiple API calls:
1 2 | // Declare Context type object for managing multiple API requests ctx, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 15*time.Second) |
How to Declare a New MongoDB Collection Instance from a Database Using the Golang Driver
Create a new MongoDB collection instance, making certain to pass the correct collection and database string names to the methods, with the following command:
1 2 3 | // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("some_database").Collection("Some Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "\n") |
How to Create a New Instance of MongoDB Fields Struct Object
Declare an instance of the Golang struct, that was setup earlier, outside of the main() function and then pass the document’s values to the respective fields with the following commands:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | // Declare a MongoDB struct instance for the document's fields and data oneDoc := MongoFields{ FieldStr: "Some Value", FieldInt: 12345, FieldBool: true, } // Should print out 'main.MongoFields' struct fmt.Println("oneDoc TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(oneDoc), "\n") |
How to Call the Golang Driver’s InsertOne Method to Insert the MongoDB Document
Use the collection instance, declared earlier, to call the mongo-go-driver package’s InsertOne() method and then pass the context instance (“ctx“) to the method call with the following commands:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | // InsertOne() method Returns mongo.InsertOneResult result, insertErr := col.InsertOne(ctx, oneDoc) if insertErr != nil { fmt.Println("InsertOne ERROR:", insertErr) os.Exit(1) // safely exit script on error } else { fmt.Println("InsertOne() result type: ", reflect.TypeOf(result)) fmt.Println("InsertOne() API result:", result) // get the inserted ID string newID := result.InsertedID fmt.Println("InsertOne() newID:", newID) fmt.Println("InsertOne() newID type:", reflect.TypeOf(newID)) } } |
The above example evaluates the object returned by the API call for errors. In the event of an API error, the error will print out and then exit the system.
The code above should print out something that resembles the following:
1 2 | InsertOne() newID: ObjectID("5d169cfa41f04dce1798020c") InsertOne() newID type: primitive.ObjectID |
The latest official MongoDB driver v1.0 uses primitive.ObjectID data types for the document _id
The result object returned by the insertion API call has an InsertedID attribute that is part of the primitive.ObjectID library and can be parsed by importing the following package library:
1 | "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson/primitive" |
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to insert a MongoDB document with Mongo-go-driver. Instructions were provided for how to import the needed MongoDB and Golang packages, how to connect to MongoDB using a Golang script, how to insertone document in MongoDB with Golang, how to create a new instance of MongoDB fields struct object and how to declare a new MongoDB collection instance from a database using the Golang driver. Remember the latest official MongoDB driver v1.0 uses primitive.ObjectID data types for the document ID.
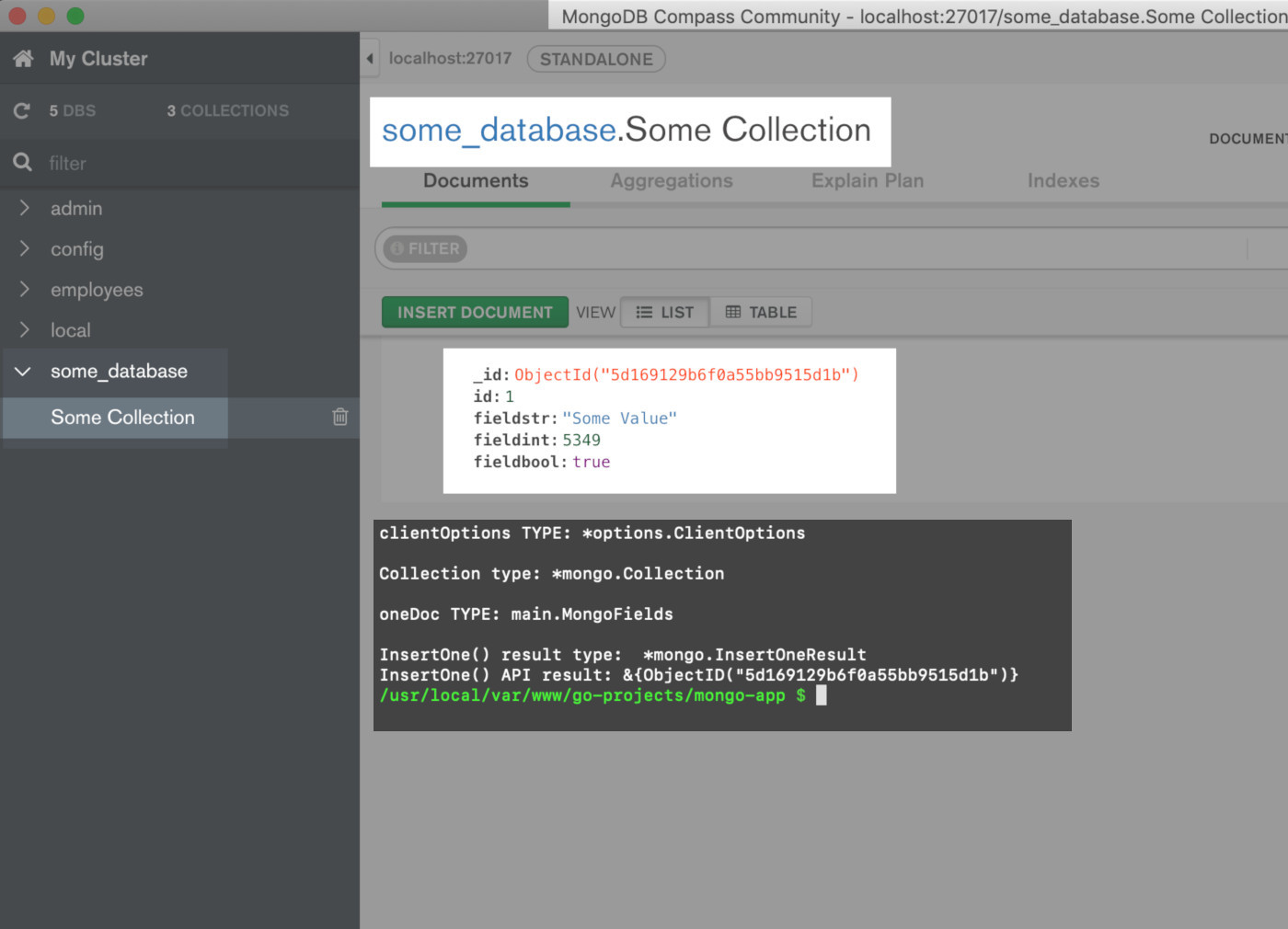
Using MongoDB Compass UI to verify that the document was inserted with the Golang script
Just the Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "os" "reflect" // get an object type "time" // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) type MongoFields struct { FieldStr string `json:"Field Str"` FieldInt int `json:"Field Int"` FieldBool bool `json:"Field Bool"` } func main() { // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "\n") // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { fmt.Println("mongo.Connect() ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } // Declare Context type object for managing multiple API requests ctx, _ := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 15*time.Second) // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("some_database").Collection("Some Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "\n") // Declare a MongoDB struct instance for the document's fields and data oneDoc := MongoFields{ FieldStr: "Some Value", FieldInt: 12345, FieldBool: true, } fmt.Println("oneDoc TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(oneDoc), "\n") // InsertOne() method Returns mongo.InsertOneResult result, insertErr := col.InsertOne(ctx, oneDoc) if insertErr != nil { fmt.Println("InsertOne ERROR:", insertErr) os.Exit(1) // safely exit script on error } else { fmt.Println("InsertOne() result type: ", reflect.TypeOf(result)) fmt.Println("InsertOne() API result:", result) // get the inserted ID string newID := result.InsertedID fmt.Println("InsertOne() newID:", newID) fmt.Println("InsertOne() newID type:", reflect.TypeOf(newID)) } } |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started



