How to Update Many MongoDB Documents Using the Golang Driver
Introduction
The tutorial will explain how to use the UpdateMany() method of the official Golang driver (mongo-go-driver) for MongoDB for updating multiple MongoDB documents in a single API call. MongoDB, Golang and the official Golang driver for MongoDB must all be installed on the same machine in order to update MongoDB documents with Go and execute the examples in this tutorial.
Prerequisites for Creating a MongoDB Index in Golang
MongoDB must be properly installed and running before beginning. Confirm MongoDB is running on the server by entering
mongo.Golang must be installed on the same machine as MongoDB and the
$GOPATHdirectory for the Golang projects must be set.The official
mongo-go-driverGolang driver for MongoDB must be installed on the same machine’s$GOPATH. Confirm this with the flowing command:
1 | go get go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo |
- Have at least one document in a MongoDB collection with data fields that can be updated.
How to Connect to MongoDB Using a Golang Script
The API call must be executed in a Golang script using the .go file extension. Create one in a folder, finder window or with the touch command in terminal.
Note that package main must be included at the top of the script.
Import the required MongoDB and Golang Packages
Use the following Go import statement to import the Golang and MongoDB packages needed to update documents:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "os" "reflect" // get an object type // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) |
How to Connect to MongoDB using the Golang Driver’s Options.Client() Method
Use the func keyword, as shown below, to declare the main() function where the data insertion and MongoDB insertOne() API call will take place:
1 | func main() { |
Connecting to MongoDB in Golang
First, declare a new options.Client() instance inside the main() function for use in creating a new connection to MongoDB.
Next, change the host and port URI settings to match the server’s domain and MongoDB settings as shown here:
1 2 3 | // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "\n") |
Now pass the clientOptions instance to the mongo.Connect() method, making sure to pass a context.TODO() object to it, as shown here:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { fmt.Println("mongo.Connect() ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } |
How to Declare a New Mongodb Collection Instance from a Database Using the Golang Driver
As shown below, create a new MongoDB collection instance, making sure to pass the correct collection and database string names to the methods:
1 2 3 | // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("some_database").Collection("Some Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "\n") |
How to Create a MongoDB Query Filter for the Golang API Calls
Declare a nested filter BSON document object, for filtering out the documents that will be updated, with the following command:
1 | filter := bson.M{"fieldint": bson.M{"$gte": 11111}} |
The above query filter will find any documents that have a "fieldint" field with an integer value greater than or equal to 11111.
Multiline MongoDB BSON query filter in Golang
Below is a more readable multiline BSON filter instantiation. It is essential to end each line with a comma to avoid the missing ',' before newline in composite literal error, as shown here:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Declare a filter to pass to the UpdateMany() method filter := bson.M{ "fieldbool": bson.M{ "$eq": true, // check if bool field has value of 'true' }, } |
The above example demonstrates how to filter MongoDB documents with a boolean value of true using BSON objects in Golang.
How to Declare a Nested BSON Object for the MongoDB Update Fields
Execute the following command to declare a Nested BSON object for the MongoDB fields that will be changed:
1 2 | // Create a nested BSON object for the updated document field update := bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"fieldstr": "ObjectRocket UPDATED!!"}} |
How to create a Golang BSON object that will update multiple MongoDB document fields
The following statement will declare a multiline nested BSON object that can update multiple fields in a MongoDB document when passed to the UpdateMany() API method call:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | // Create a nested BSON document for the documents' fields that are updated update := bson.M{ "$set": bson.M{ "fieldstr": "ObjectRocket UPDATED!!", "fieldbool": false, }, } |
How to Request the UpdateMany() Method Call to Update Multiple MongoDB Documents
The last step in the process is to pass both the filter and the update nested BSON objects, as well as a context object, to the MongoDB collection instant’s UpdateMany() method with the following command:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | // Call the driver's UpdateMany() method and pass filter and update to it result, err := col.UpdateMany( context.Background(), filter, update, ) |
A fourth “Option” parameter can also be passed to the method call for more API options. Have the API call return both a result and error response.
How to Check for Errors and the UpdateMany() MongoDB API Results
Execute the following command to evaluate the err object to find out if MongoDB returned any errors:
1 2 3 4 | // Check for error, else print the UpdateMany() API call results if err != nil { fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) // Exit |
Parse the MongoDB Golang driver’s API results object
Print out the parsed results of the API call, as shown here, if no errors are found:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | } else { fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result:", result) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(result)) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result MatchedCount:", result.MatchedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result ModifiedCount:", result.ModifiedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result UpsertedCount:", result.UpsertedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result UpsertedID:", result.UpsertedID) } |
The result object’s attributes should have several integer value attributes representing the documents that matched the filter, the documents that were modified and information about any upserted MongoDB documents in the process of the API call.
Conclusion
This tutorial covered how to update MongoDB documents with the Golang driver. Specifically, how to declare a new MongoDB collection instance from a database using the Golang driver, create a MongoDB query filter for the Golang API calls, how to declare a nested BSON object for the MongoDB update fields and create a Golang BSON object that will update multiple fields. Finally, the article explained how to check for errors and parse the MongoDB Golang driver’s API results object. Remember, to update MongoDB documents there must be at least one document in a MongoDB collection with data fields that can be updated. To update documents with Mongo-Go-driver the API call must be executed in a Golang script using the .go file extension.
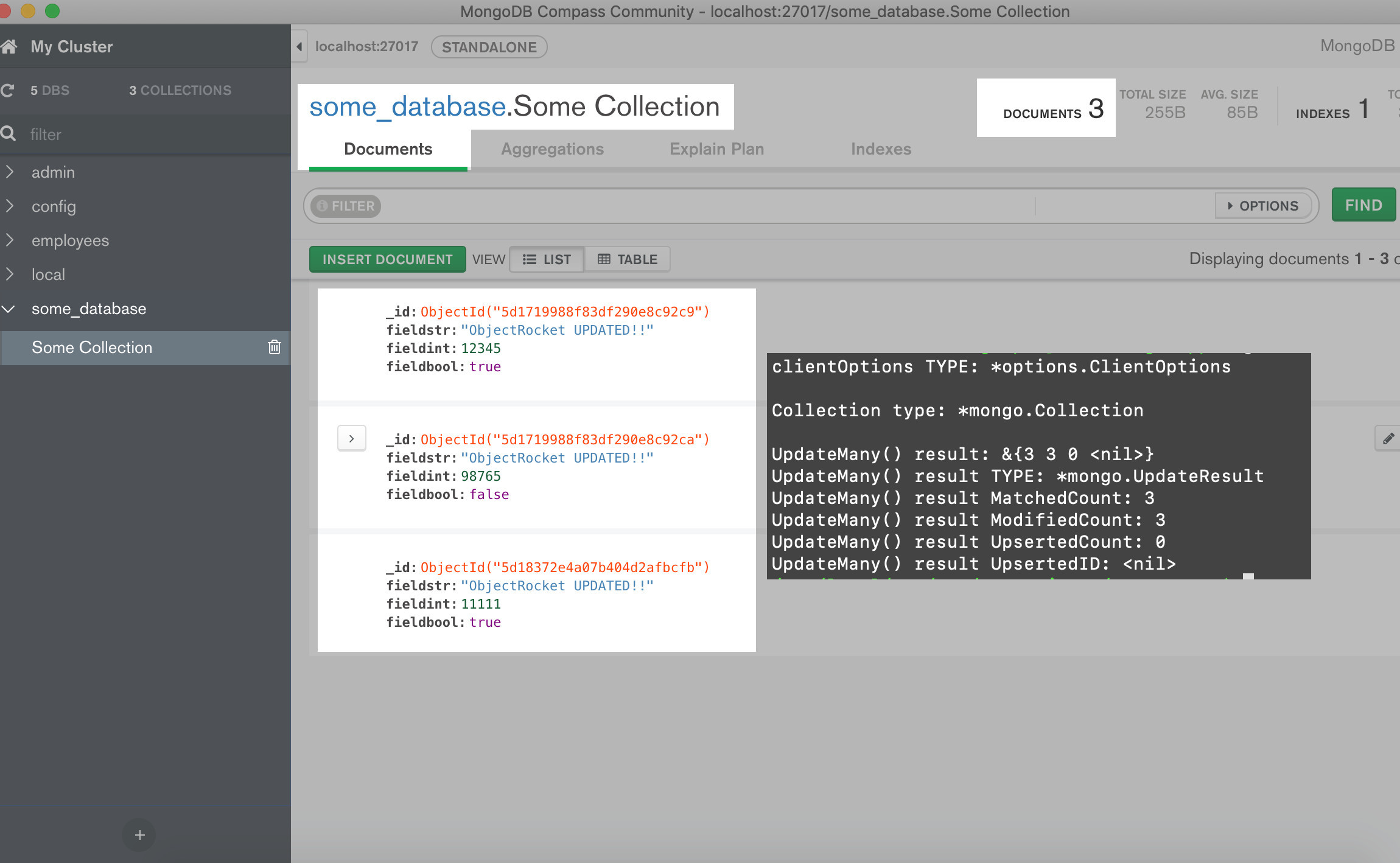
How to use MongoDB Compass UI to verify that documents were updated using UpdateMany() in Golang
The following is a screenshot of the MongoDB Compass UI displaying the updated documents:
Just the Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 | package main import ( // Built-in Golang packages "context" // manage multiple requests "fmt" // Println() function "os" "reflect" // get an object type // Official 'mongo-go-driver' packages "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/bson" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo" "go.mongodb.org/mongo-driver/mongo/options" ) func main() { // Declare host and port options to pass to the Connect() method clientOptions := options.Client().ApplyURI("mongodb://localhost:27017") fmt.Println("clientOptions TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(clientOptions), "\n") // Connect to the MongoDB and return Client instance client, err := mongo.Connect(context.TODO(), clientOptions) if err != nil { fmt.Println("mongo.Connect() ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) } // Access a MongoDB collection through a database col := client.Database("some_database").Collection("Some Collection") fmt.Println("Collection type:", reflect.TypeOf(col), "\n") // Declare a filter to pass to the UpdateMany() method filter := bson.M{"fieldint": bson.M{"$gte": 11111}} // Create a nested BSON object for the updated document field update := bson.M{"$set": bson.M{"fieldstr": "ObjectRocket UPDATED!!"}} // Declare a filter to pass to the UpdateMany() method /* filter := bson.M{ "fieldbool": bson.M{ "$eq": true, // check if bool field has value of 'true' }, } // Create a nested BSON document for the documents' fields that are updated update := bson.M{ "$set": bson.M{ "fieldstr": "ObjectRocket UPDATED!!", "fieldbool": false, }, } */ // Call the driver's UpdateMany() method and pass filter and update to it result, err := col.UpdateMany( context.Background(), filter, update, ) // Check for error, else print the UpdateMany() API call results if err != nil { fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result ERROR:", err) os.Exit(1) // Exit the script on error } else { fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result:", result) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result TYPE:", reflect.TypeOf(result)) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result MatchedCount:", result.MatchedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result ModifiedCount:", result.ModifiedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result UpsertedCount:", result.UpsertedCount) fmt.Println("UpdateMany() result UpsertedID:", result.UpsertedID) } } |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started


