How To Create and Setup a MongoDB Collection in Python
Introduction
This tutorial will explain how to create a collection in MongoDB database using the Python PyMongo driver and provide examples of working with PYMongo collations, PYMongo collections and Python MongoDB collections. PYMongo collections are a group of documents saved in a MongoDB database, similar to a table in a SQL database. PyMongo is a Python distribution that incorporates the necessary tools for working with a Python MongoDB Collection. PYMongo collations provide a set of rules for comparing strings that follow the pattern of a specific language, or when setting certain restrictions.
Prerequisites
- A working knowledge of Python and its syntax.
- The properly installed Python interpreter.
Note: As Python 2.7 is deprecated and scheduled to lose long-term support by 2020, all examples in this tutorial were executed with Python 3.
The MongoDB server application must be properly installed. Confirm this by excuting the
mongo --versioncommand in a terminal, or enter the Mongo shell in a terminal by typingmongoand then pressing the “Return” key.The low-level PyMongo Python driver for MongoDB must be installed with the PIP package manager, as shown here:
1 | pip3 install pymongo |
How to Create a MongoDB Client Instance and Database Using Python
Import the MongoClient class and create a new client instance of the driver. As shown here:
1 2 | from pymongo import MongoClient mongo_client = MongoClient() |
Now use the mongo_client object to make method calls to a MongoDB database and its collections
Setup Collations for the MongoDB Collection Using a Python Dictionary
Use collations to add language and geographic-specific restrictions to a MongoDB collection’s data.
Collation parameters
The structure of a MongoDB collection’s collation follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | { locale: <string>, # "en_US", "zh_CN", "es_ES" caseLevel: <boolean>, caseFirst: <string>, strength: <int>, numericOrdering: <boolean>, alternate: <string>, maxVariable: <string>, backwards: <boolean> } |
>NOTE: Collations with collections are only supported in MongoDB v3.4 or newer.
The proper format for the ISO language codes in a MongoDB Collation uses underscores (e.g. en_US) and not hypens (e.g. "en-US").
How to Create a MongoDB Collation in Python
Below is a basic example of how a collation would look in Python. The first step is to import the Collation class from the pymongo.collation library, as follows:
1 | from pymongo.collation import Collation |
Pass the parameters for the collation into the Collation() method directly and have it return a pymongo.collation.Collation object, as shown here:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | colla = Collation( locale = "en_US", strength = 2, numericOrdering = True, backwards = False ) |
Alternatively, create a simple Python dict object, setting all of the parameters for the collation as the dict keys, and pass that dictionary to the create_collection() method instead, as shown here:
1 | colla = {'locale': 'en_US', 'strength': 2, 'numericOrdering': True, 'backwards': False} |
How to Call the PyMongo Create_Collection() Method to Create a MongoDB Collection in Python
Once the collation object, or dictionary, has been declared, then call the create_collection() method to create a MongoDB collection.
Access a MongoDB database
Create an instance of a MongoDB database so PyMongo will be able to determine what database the new collection will be added to, as follows:
1 | db = mongo_client["Test-Database"] |
How to call the database object’s create_collection() method
Take the collation object from the above example and pass it to the db.create_collection() method’s collation parameter, as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | col = db.create_collection( name="Collation-Test", codec_options=None, read_preference=None, write_concern=None, read_concern=None, session=None, collation=colla ) |
>NOTE: All of the optional parameters will default to None if no arguments are passed for the parameters.
The API call should return a pymongo.collection.Collection object that can be used to make other API calls, such as indexing documents to the collection.
PyMongo returns CollectionInvalid: <span>collection Collation-Test already exists error
PyMongo will raise an exception if the collection already exists. To work around this, use a try-except indentation block, as follows:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 | try: col = db.create_collection( name=collection_name, codec_options=None, read_preference=None, write_concern=None, read_concern=None, session=None, collation=colla ) except Exception as err: # collection already exists if "already exists" in err._message: col = db[collection_name] else: print ("create_collection() ERROR:", err) col = None print ("Collection name:", col.name) |
How to Verify the Collection and its New Collation Using the MongoDB Compass UI
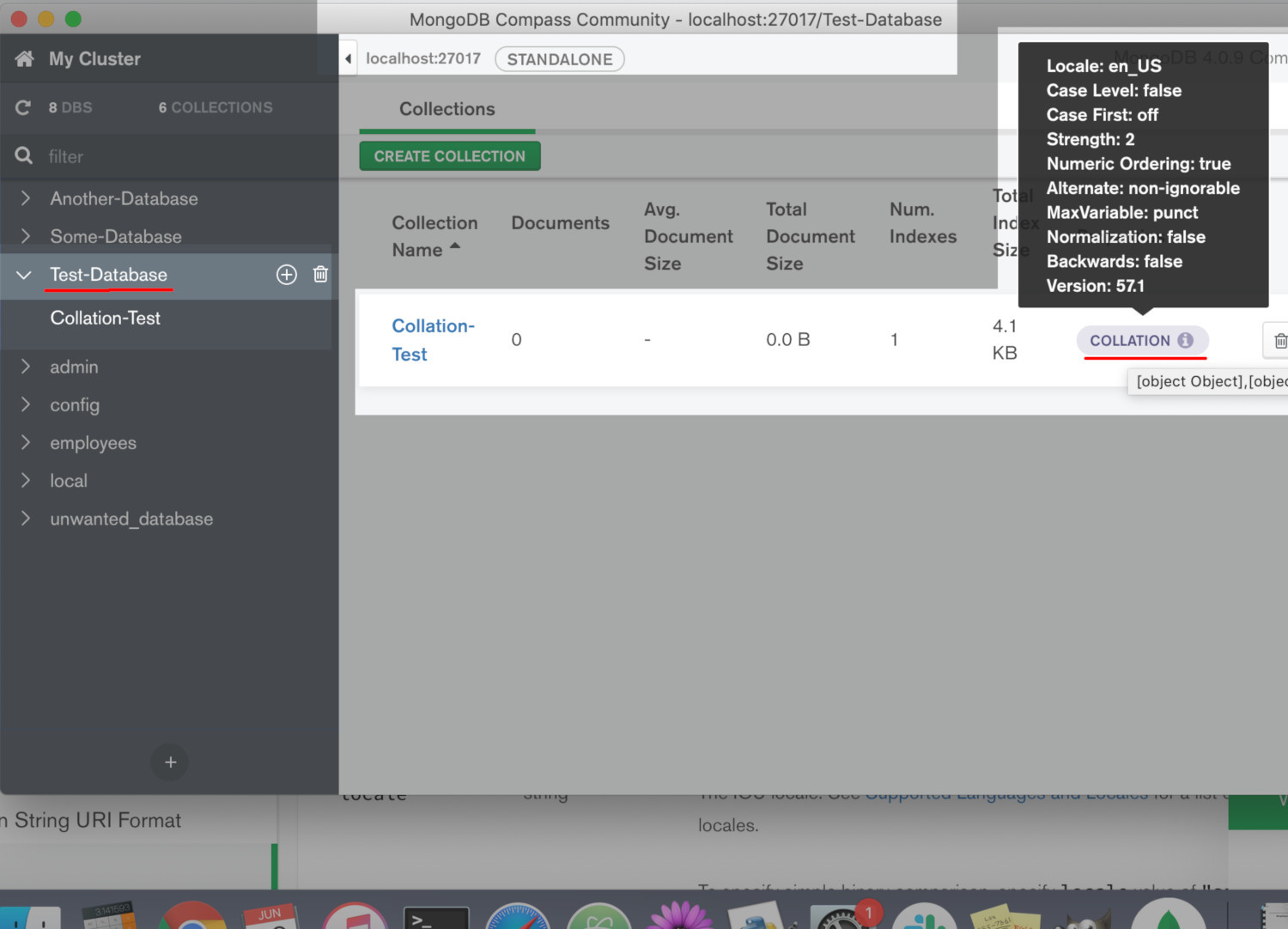
Open the MongoDB Compass app, if installed, to verify the collection was successfully created. Click on the name of the database used to create a new collection and hover the curser over the “Collation” button on the right-hand side of the image, as shown below, to get more information.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to set up and use collations in MongoDB to create a collection in Python with the PyMongo driver. PYMongo collations are used to add language and geographic-specific restrictions on a MongoDB collection’s data. Bear in mind, collations with Mongo collections are only supported in MongoDB v3.4 or newer. Python Version 3 was used for all examples in this tutorial and results may vary if using an earlier version of Python.
Just the Code
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 | #!/usr/bin/env python3 #-*- coding: utf-8 -*- # import the MongoClient class and 'errors' module from pymongo import MongoClient # import the Collation module for PyMongo from pymongo.collation import Collation # create a collation object for the new collection colla = Collation( locale = "en_US", strength = 2, numericOrdering = True, backwards = False ) # dictionary version of the same collation # colla = {'locale': 'en_US', 'strength': 2, 'numericOrdering': True, 'backwards': False} # create a client instance of the MongoClient class mongo_client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017') # create a database instance from the client db = mongo_client["Test-Database"] # call the database object's create_collection() method col = db.create_collection( name="Collation-Test", codec_options=None, read_preference=None, write_concern=None, read_concern=None, session=None, collation=colla ) |
Pilot the ObjectRocket Platform Free!
Try Fully-Managed CockroachDB, Elasticsearch, MongoDB, PostgreSQL (Beta) or Redis.
Get Started


